10 years since world health report "Health systems financing: the path to universal health coverage"
-1.png?sfvrsn=872dd4cb_3)
-1.png?sfvrsn=a7b784e6_5)
Launched a Universal Coverage UHC scheme in 2012, which resulted in 98% of the population with coverage, at a cost to the Government of US$ 80 per beneficiary
Because we are poor, we cannot afford not to have universal health coverage.
Thai Minister of Public Health on Universal Health Coverage Day, 2016

Launched a Universal Coverage UHC scheme in 2012, which resulted in 98% of the population with coverage, at a cost to the Government of US$ 80 per beneficiary
Because we are poor, we cannot afford not to have universal health coverage.
Thai Minister of Public Health on Universal Health Coverage Day, 2016
Large, predominantly government participation in health care and services in public facilities provided free at point of delivery and little private expenditure; however, financial hardship due to large household expenditure on health has slightly increased.
| Coverage of essential services | < 10% household expenditure on health |
|---|---|
| Improved from 24/100 (2000) to 52/100 (2017) | Worsened from 2.6% (2001) to 2.9% (2014) |
Coverage of essential services should be improved; e.g. only 57% of births are attended by skilled personnel and only 73.5% of children are fully vaccinated by 12 months of age.
*

Large, predominantly government participation in health care and services in public facilities provided free at point of delivery and little private expenditure; however, financial hardship due to large household expenditure on health has slightly increased.
| Coverage of essential services | < 10% household expenditure on health |
|---|---|
| Improved from 24/100 (2000) to 52/100 (2017) | Worsened from 2.6% (2001) to 2.9% (2014) |
Coverage of essential services should be improved; e.g. only 57% of births are attended by skilled personnel and only 73.5% of children are fully vaccinated by 12 months of age.
*
Tripled public spending on health in a decade, increasing public expenditure on primary health care to 37%, as compared with a regional average of < 15%
| Coverage of essential services | > 10% household expenditure on health |
|---|---|
| Improved from 41/100 (2000) to 68/100 (2017) | Improved from 11.06% (2000) to 6.02% (2016) |
1 in 3 Latin American countries close to reaching the goal of allocating 6% of GDP towards public health.

Tripled public spending on health in a decade, increasing public expenditure on primary health care to 37%, as compared with a regional average of < 15%
| Coverage of essential services | > 10% household expenditure on health |
|---|---|
| Improved from 41/100 (2000) to 68/100 (2017) | Improved from 11.06% (2000) to 6.02% (2016) |
1 in 3 Latin American countries close to reaching the goal of allocating 6% of GDP towards public health.

WHO launches Health Financing Progress Matrix to monitor
policies that directly contribute
to improved financial protection and service coverage

3rd global monitoring report shows divergent progress towards UHC since 2000:
catastrophic health spending
and recommends
United Nations Member States adopt high-level political declaration to ensure that everyone has access to essential health services without experiencing financial hardship
Support provided:
- options for a health financing policy;
- knowledge on crucial aspects and implications of a new policy, including governance financing, management of health services and integrated health service networks; and
- facilitation of discussions with stakeholder to ensure buy-in to a new policy

2nd global monitoring report shows:
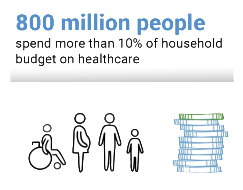

1st global monitoring report tracks countries’ progress towards universal health coverage:
.png?sfvrsn=e49c8af_3)
Resolution WHA64.9 requests the Director-General to approve a plan of action to support Member States in realizing universal coverage as envisaged by the World Health Report 2010
Member States urged to ensure health financing is available to implement policies to avoid catastrophic health-care expenditure and impoverishment as a result of seeking care.
The World Health Report 2010 on health systems financing provides a
road map
to achieving universal health coverage after the global financial crisis in 2009
