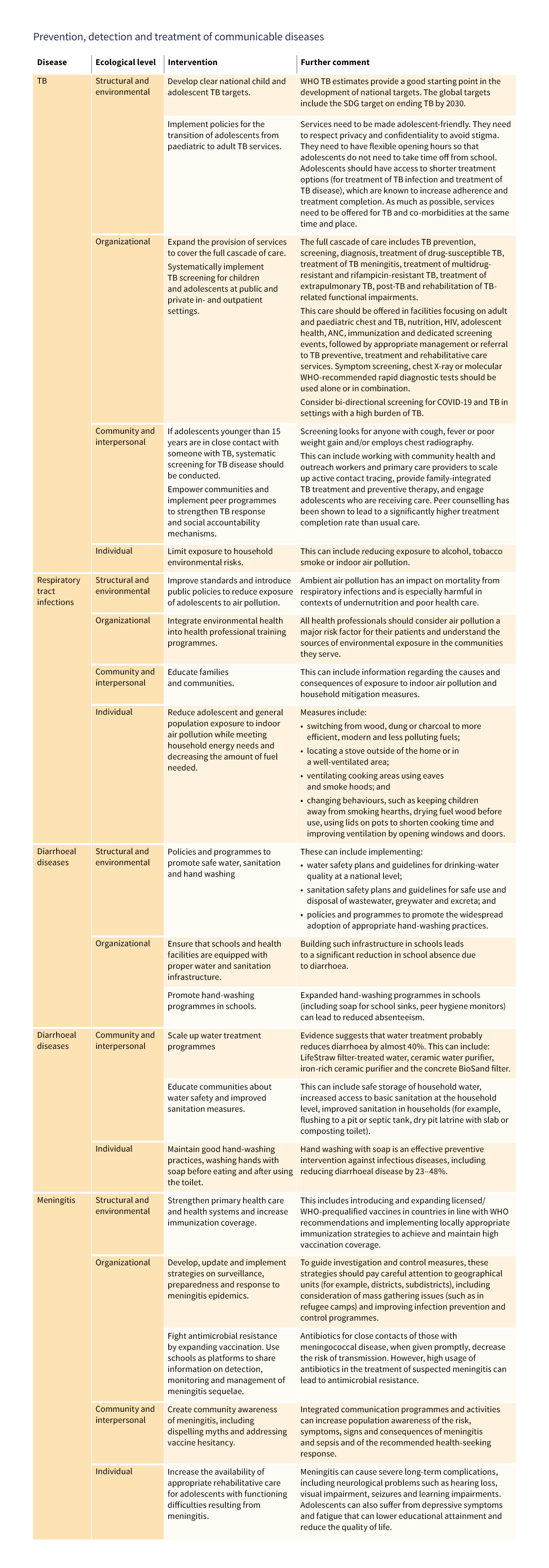
As described in Chapter 2, infectious diseases (such as TB and respiratory infections) remain the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in LMICs. Interventions to improve case detection and management of high-burden diseases in this age group are crucially needed. In some cases, for example, water and sanitation interventions to prevent diarrhoeal disease can be easily expanded along the lines of those for younger children. In other cases, such as for vaccinations, further attention may be needed to ensure that the unique needs and vulnerabilities of adolescents are addressed.
Routine immunization is an important public health strategy to address a number of vaccine-preventable diseases. The benefits of vaccination go beyond early childhood, continuing through adolescence. In addition to the HPV vaccine, which is the vaccine most commonly associated with adolescents, other vaccines administered for adolescents include tetanus–diphtheria, seasonal influenza, cholera, dengue, rabies, typhoid, COVID-19 (see Box below) and meningitis. Promising vaccines are in the pipeline against respiratory syncytial virus, malaria, TB and all influenza virus strains.
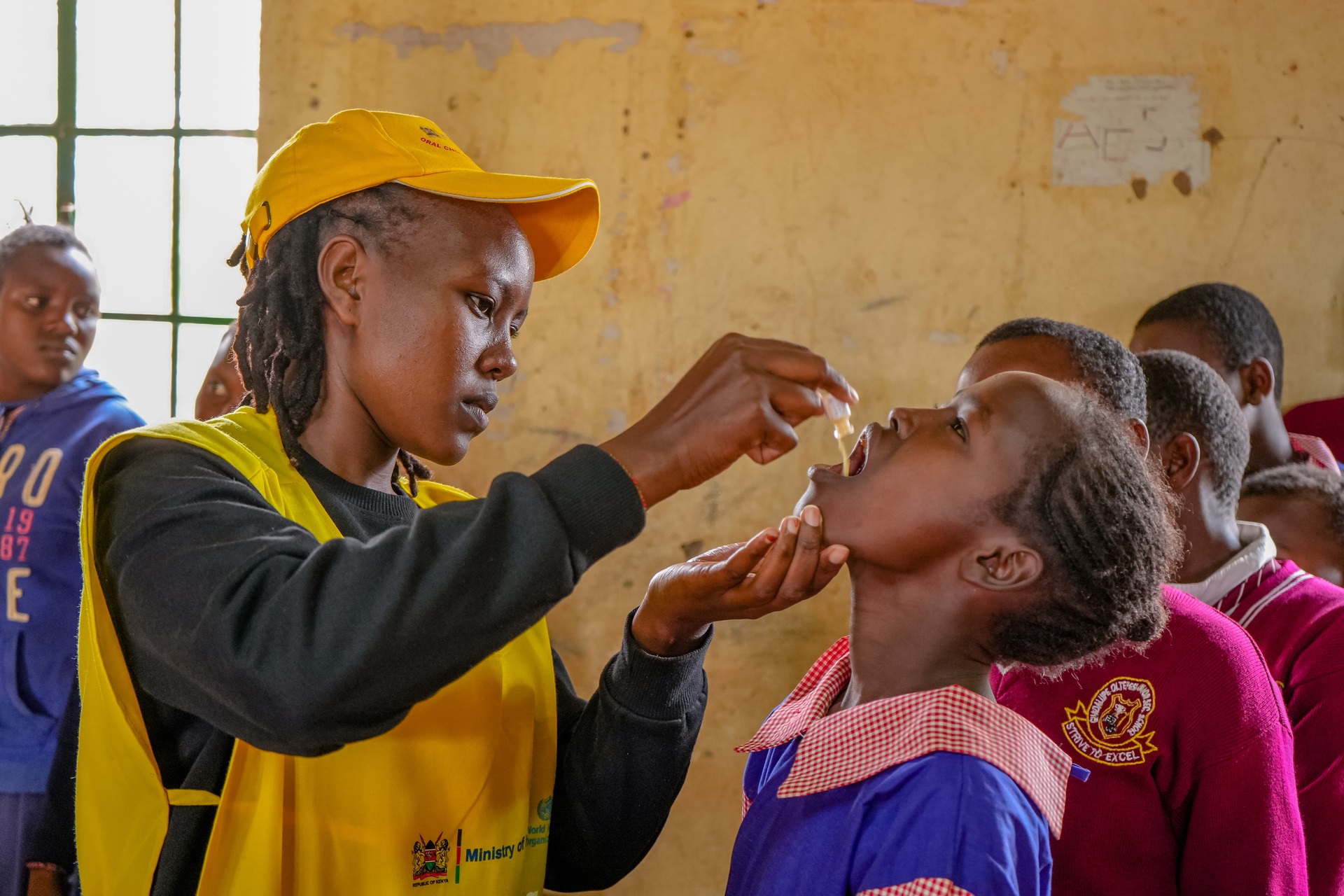
Faith, a vaccinator from Mashuuru, administers oral cholera vaccine (OCV) to a student in Guadalupe Oltepesi Primary School during the OCV campaign in Kajiado on 4 August 2023.