Influenza Update N° 455

Overview
2 October 2023, based on data up to 17 September 2023
Information in this report is categorized by influenza transmission zones, which are geographical groups of countries, areas or territories with similar influenza transmission patterns. For more information on influenza transmission zones, see the link below:
Influenza Transmission Zones (pdf, 659kb)
- Countries are recommended to monitor the relative co-circulation of influenza and SARS-CoV-2 viruses in integrated surveillance and report to RespiMART (FluNet and FluID) directly or via regional platforms. Clinicians should consider influenza in differential diagnosis, especially for high-risk groups for influenza, and test and treat according to national and WHO guidance.
- Globally, influenza detections remained low.
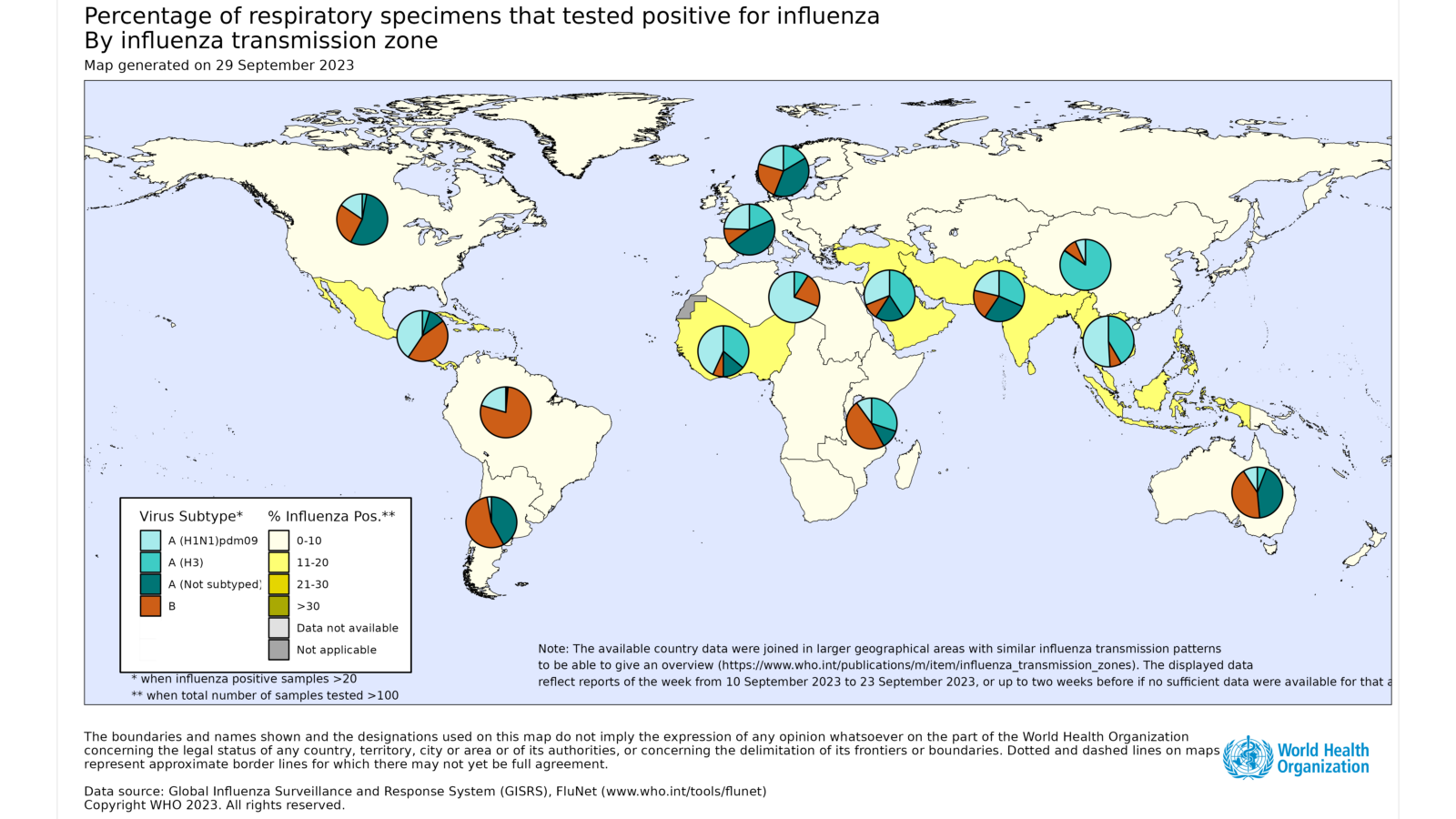
- In Oceania, influenza activity decreased with influenza A(H1N1)pdm09, influenza A(H3N2) and influenza B viruses all cocirculating.
- In South Africa, influenza activity remained below the seasonal threshold after peaking in early June, although detections of influenza B/Victoria lineage increased in recent weeks.
- In temperate South America, influenza detections remained low overall with A and B viruses co-circulating.
- In the Caribbean countries, influenza activity remained low overall.
- In the Central American countries, influenza activity decreased overall with influenza B viruses and influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses predominant.
- overall influenza activity was low with detections of predominantly influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and B viruses.
- In tropical Africa, all seasonal influenza subtypes co-circulated. Influenza detections remained low in Middle and Eastern Africa, but increased in some countries in Western Africa.
- In Southern Asia, influenza activity remained low overall except in Bangladesh and Bhutan where activity was elevated but decreasing.
- In South-East Asia, influenza activity remained elevated overall, with continued reporting of predominantly influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and A(H3N2) virus detections.
- In the temperate zones of the northern hemisphere, indicators of influenza activity were reported at low levels or below seasonal threshold in most reporting countries. Detections were predominantly influenza A(H3N2) followed by influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and B viruses.
- National Influenza Centres (NICs) and other national influenza laboratories from 107 countries, areas or territories reported data to FluNet for the time period from 04 September 2023 to 17 September 2023* (data as of 29/09/2023 07:23:47 AM UTC). The WHO GISRS laboratories tested more than 298 993 specimens during that time period. 7773 were positive for influenza viruses, of which 6247 (80.37%) were typed as influenza A and 1526 (19.63%) as influenza B. Of the sub-typed influenza A viruses, 1383 (28.87%) were influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and 3407 (71.13%) were influenza A(H3N2). Of the type B viruses for which lineage was determined, all (606) belonged to the B/Victoria lineage.
- Globally, SARS-CoV-2 positivity from sentinel surveillance decreased a little and was around 10%. Activity was stable at around 13% in the Region of the Americas, decreased to around 15% in the European Region and increased to around 10% in the Eastern Mediterranean Region and Western Pacific Region. Positivity remained below 10% in the African and South-East Asia Regions. SARS-CoV-2 positivity from non-sentinel surveillance decreased but remained above 10% globally.
- From countries with RSV surveillance in place, RSV activity was generally low except in Western Australia and some countries in central America and temperate South America.
- WHO encourages countries, especially those that have received the multiplex influenza and SARS-CoV-2 reagent kits from GISRS, to conduct integrated surveillance of influenza and SARS-CoV-2 and report epidemiological and laboratory information in a timely manner to established regional and global platforms. The guidance can be found here: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-integrated_sentinel_surveillance-2022.1.
- National Influenza Centres (NICs) and other national influenza laboratories from 71 countries, areas or territories from six WHO regions (African Region: 12; Region of the Americas: 18; Eastern Mediterranean Region: 4; European Region: 25; South-East Asia Region: 5; Western Pacific Region: 7) reported to FluNet from sentinel surveillance sites for time period from 04 September 2023 to 17 September 2023* (data as of 29/09/2023 07:23:47 AM UTC). The WHO GISRS laboratories tested more than 30 331 sentinel specimens during that time period and 3033 (10.00%) were positive for SARS-CoV-2. Additionally, more than 42 560 non-sentinel or undefined reporting source samples were tested in the same period and 6410 were positive for SARS-CoV-2. Further details are included at the end of this update.
Source of data
______________________________________________________________________________________________
The Global Influenza Programme monitors influenza activity worldwide and publishes an update every two weeks. The updates are based on available epidemiological and virological data sources, including FluNet (reported by the WHO Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System), FluID (epidemiological data reported by national focal points) and influenza reports from WHO Regional Offices and Member States. Completeness can vary among updates due to availability and quality of data available at the time when the update is developed.
*It includes data only from countries reporting on positive and negative influenza specimens.
