Global Routine Immunization Strategies and Practices (GRISP)
Immunizations are among the most successful and cost-effective health interventions ever devised. They have reduced child deaths and disease prevalence radically. They have enabled the eradication of smallpox, lowered the global incidence of polio by more than 99% and neonatal tetanus by 94%, and achieved dramatic reductions in illness, disability and death from common childhood diseases. However, global mobility and interdependence have increased the vulnerability of people everywhere to the uncontrolled spread of diseases through epidemics.
To realize the full benefits of immunization, the Global Vaccine Action Plan 2011–2020 (GVAP), endorsed by the World Health Assembly in May 2012, sets the direction for a “Decade of Vaccines” through delivery of universal access to immunization.
The term “routine immunization” is understood in two distinct ways that relate to the foundation of the health system and activities to improve equitable coverage. It is important to distinguish between these perspectives, as many activities to sustainably strengthen routine immunization systems may not result in short-term or rapid improvements in immunization coverage. Equally, many activities specifically designed to rapidly increase routine immunization coverage may not result in the long-term strengthening and sustainability of the programme.
The purpose of GRISP is to reassert routine immunization as the foundation for sustained decreases in morbidity and mortality from vaccine-preventable...
GRISP contains two components:
- nine transformative investments to achieving better immunization outcomes and,
- a comprehensive framework of strategies and practices for routine immunization.
Nine transformative investments to achieving better immunization outcomes
These aim to provide overall direction and, if implemented, will transform national programmes and the work of global partners, enabling us to reach the stated DoV goals. These investments are a call to action to governments, donors and partners and should be seen as the highlights and priorities of this document.
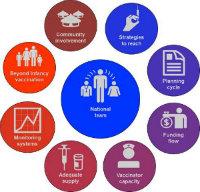
The nine transformative investments are:
- Invest in a capable national team – supplied with sufficient resources and authority – to expertly manage each country’s national immunization programme.
- Invest in tailored strategies that identify undervaccinated and unvaccinated persons and regularly provide them with the vaccines they need.
- Invest in a coherent planning cycle, with strategic, comprehensive, multi-year and operational annual plans outlining and coordinating strategies and activities, which are monitored quarterly.
- Invest in ensuring that sufficient and adequately appropriated funds reach the operational level of the programme regularly.
- Invest in vaccinators and district managers by regularly and systematically building their capacity, strengthening their performance and providing supportive supervision.
- Invest in modernizing vaccine supply chains and management to ensure that the correct amounts of the right potent vaccines are available at each vaccination session.
- Invest in an information system that identifies and tracks each person’s vaccination status.
- Invest in sustainably expanding routine vaccination schedules to cover people’s entire lives.
- Invest in the shared responsibility for immunization delivery between communities and the immunization programme to reach uniformly high coverage through high demand and quality services.
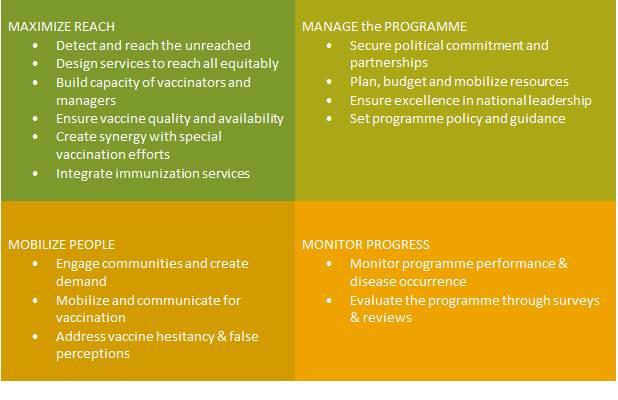
A comprehensive framework of strategies and practices for routine immunization
Implementing the strategies and practices within this framework will strengthen routine immunization systems and improve coverage. In addition, the framework organizes them by four main areas of action, enabling a systematic approach to be taken.