/noncommunicable-diseases-rehabilitation-and-disability-(ncd)/office-of-the-director-ncd-(odn)/ncds-knowledge-action-portal.jpg?sfvrsn=d75056b8_4)
Knowledge Action Portal on NCDs
Take a look behind the scenes of the Knowledge Action Portal (KAP).
/noncommunicable-diseases-rehabilitation-and-disability-(ncd)/office-of-the-director-ncd-(odn)/ncds-knowledge-action-portal.jpg?sfvrsn=d75056b8_4)
Take a look behind the scenes of the Knowledge Action Portal (KAP).
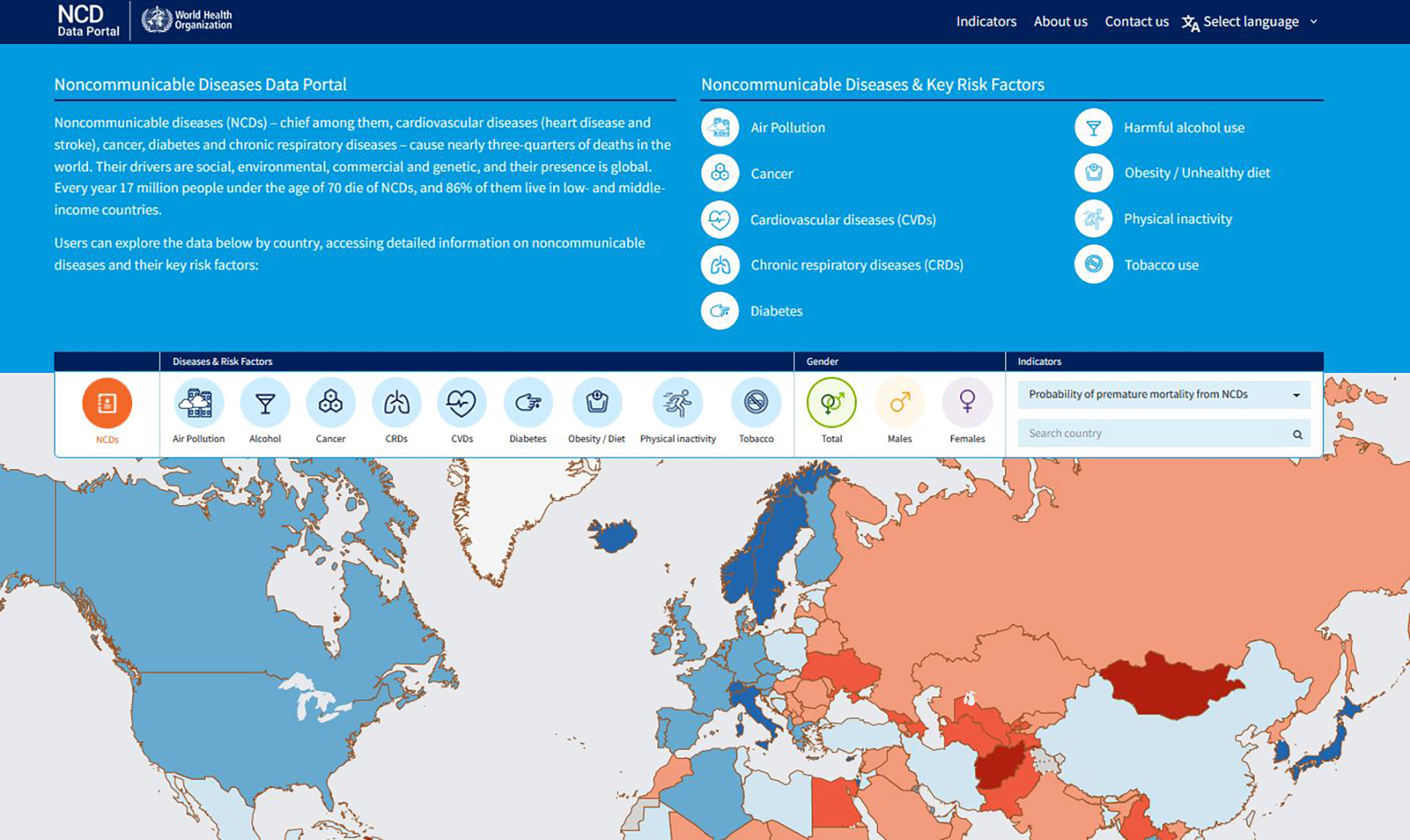
Explore the data by country
/noncommunicable-diseases-rehabilitation-and-disability-(ncd)/office-of-the-director-ncd-(odn)/on-the-road-to-2025-countdown-days.jpg?sfvrsn=7d7b21e4_79)
Preparatory process for the Fourth High-level Meeting of the UN General Assembly on the prevention and control of NCDs (HLM4)
/noncommunicable-diseases-rehabilitation-and-disability-(ncd)/office-of-the-director-ncd-(odn)/un-general-assembly-meeting-room.jpg?sfvrsn=b07fcc1d_7)
for the Global action plan for the prevention and control of NCDs 2013–2030
Related health topics
Noncommunicable diseases
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death globally, taking an estimated 19.8 million lives each year. CVDs are a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels and include coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, rheumatic heart disease and other conditions. More than four out of five CVD deaths are due to heart attacks and strokes, and one third of these deaths occur prematurely in people under 70 years of age.
The most important behavioural risk factors of heart disease and stroke are unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, tobacco use and harmful use of alcohol. The effects of behavioural risk factors may show up in individuals as raised blood pressure, raised blood glucose, raised blood lipids, and overweight and obesity. These “intermediate risks factors” can be measured in primary care facilities and indicate an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, heart failure and other complications.
Cessation of tobacco use, reduction of salt in the diet, eating more fruit and vegetables, regular physical activity and avoiding harmful use of alcohol have been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Health policies that create conducive environments for making healthy choices affordable and available are essential for motivating people to adopt and sustain healthy behaviours.
Identifying those at highest risk of CVDs and ensuring they receive appropriate treatment can prevent premature deaths. Access to noncommunicable disease medicines and basic health technologies in all primary health care facilities is essential to ensure that those in need receive treatment and counselling.
Technical links
Sensory functions, disability and rehabilitation
Risk factors
Other related health topics
The Framework for the care of acute coronary syndrome and stroke aims to guide countries in strengthening the care of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and...
A framework for action provides a guide for those involved in the development of the multisectoral action plan. It starts with a wide-ranging vision and,...
This toolkit is a "how to" guide for developing, implementing and evaluating a multisectoral action plan for prevention and control of NCDs. It is targeted...
To maintain a structured and well-organized implementation plan it is important to have a lead agency or sector. The ministry of health or a similar...
When considering a multisectoral action plan (MSAP), it is important to take into account various issues relating to its implementation. Implementation is...
One of the first steps in developing a multisectoral action plan (MSAP) is to use a situation analysis to provide a comprehensive assessment...
Key stakeholders must be involved in the planning, implementation, monitoring and evaluation of NCD plans and programmes. Within a ministry of health there...
High blood pressure kills more people than any other condition – approximately 10 million people each year, more than all infectious diseases combined....
Feature stories
Fact sheets
Engagement with the private sector
Noncommunicable diseases and COVID-19
