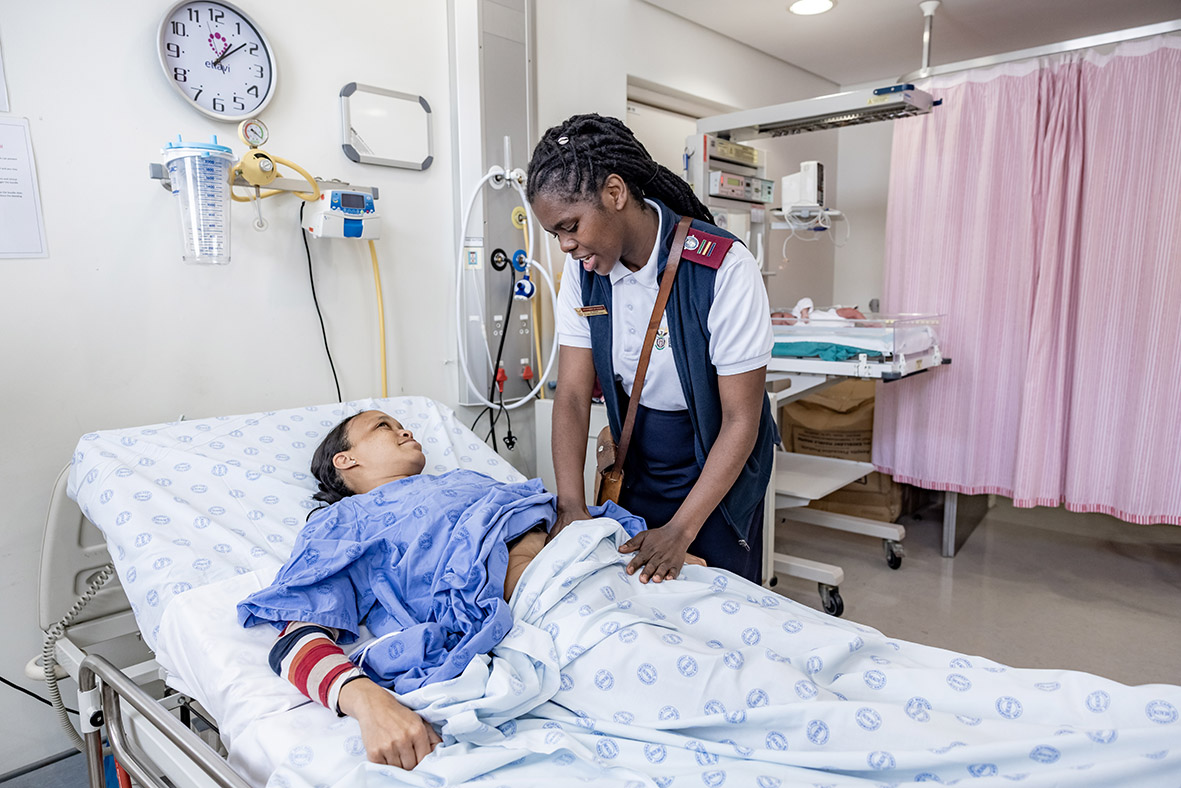

Preventing, detecting and treating the leading cause of maternal mortality
The Bleeding after birth training course aims to translate standards into care. It incorporates the latest WHO recommendations related to postpartum haemorhage (PPH) and includes links to key references and resources for training. This course is for all health workers who care for women at birth. All women should give birth in facilities with the capacity to treat PPH, and administer intravenous (IV) medicines.
As part of the learning process, the course includes pre‑course and post‑course knowledge checks, and objective structured clinical examinations (OSCEs).
Demonstration videos from Global Health Media, available to view online and download. For use during the course and after for continued practice.
Sample documents for organizers and facilitators – like agendas, room layouts, checklists and evaluations. Download and adapt to fit your needs.
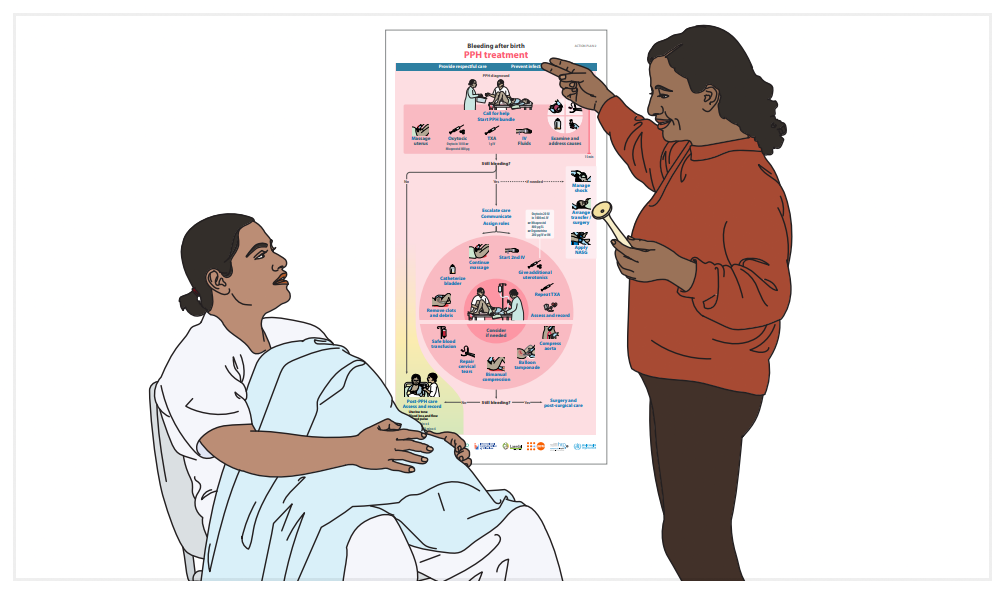
The facilitated course using the Flipchart uses a hands-on, team-oriented, and facility-based approach to learning.
The training materials are designed for small group instruction, ensuring personalized attention and a greater impact on skill acquisition and retention.
The educational principles promote continuous learning through:
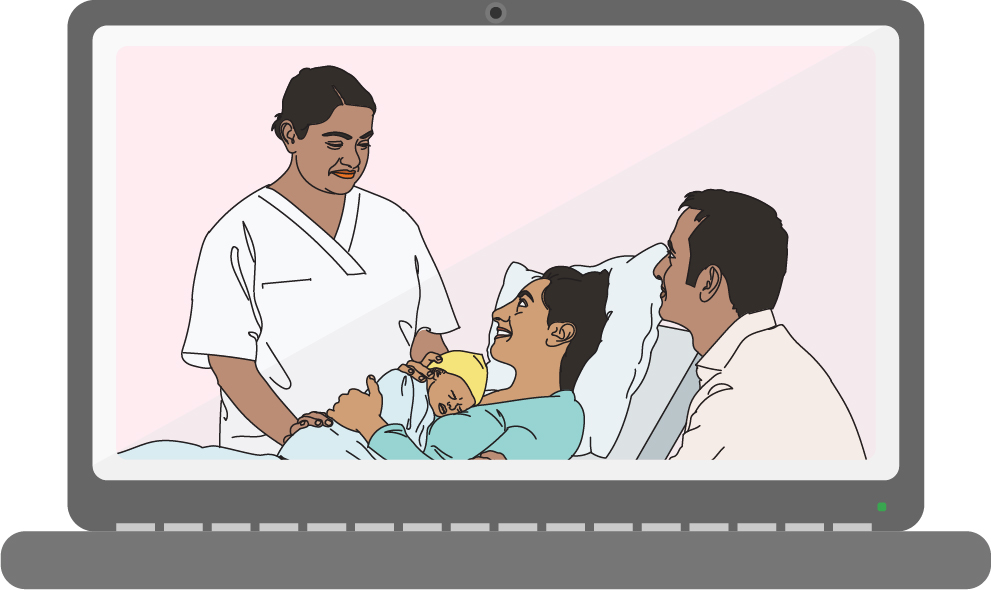
The e-learning course on the WHO Academy allows participants to do a portion of the course on their own. They can review the content and check their knowledge through interactive activities.
After completing the e-learning, participants can take part in hands-on practice with a mentor or facilitator.
Papageorghiou, Aris TAhsan, Sadiah et al. New guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage: ending the geography of risk. The Lancet Global Health. Published online October 4, 2025.
Gallos, Ioannis et al. Prognostic accuracy of clinical markers of postpartum bleeding in predicting maternal mortality or severe morbidity: a WHO individual participant data meta-analysis. The Lancet. Published online October 4, 2025.
PPH Roadmap Advocacy Working Group. World postpartum hemorrhage day: Renewing the global call to end deaths from postpartum hemorrhage. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. Published online October 3, 2025. doi:10.1002/ijgo.70550

Preventing, detecting and treating the leading cause of maternal mortality

