Workload Indicators of staffing need (WISN)
The health workforce is the fulcrum on which health system performance relies. Human resources for health as a strategic area of focus is crucial to affordable, accessible and high-quality health services. The ability of a country to meet its health commitments and goals largely depends on the number, skills, competencies and availability of health workers, and on whether those workers are organized and equitably distributed to deliver integrated, people-centred health services. The health workforce is essential to achieving universal health coverage and the Sustainable Development Goals, especially Indicator 3.c.1, which relates to ”health workforce density and distribution” and improved data on human resources for health.
Health service managers around the world face increasing HRH challenges, such as:
- inadequate resources to respond to the populations’ demand for services;
- the distribution of human resources being generally poorly balanced between urban and rural areas, and between primary, secondary and tertiary levels of care;
- inefficiencies due to uncoordinated HRH practices from various stakeholders; and
- weak HRH coordination mechanisms and weak human resources for health information systems.
The Workload Indicators of Staffing Need (WISN) method is based on a health worker’s workload, with activity (time) standards applied for each workload component. This principle has long been used in business but was not employed in the health sector until the late 1990s, when the WISN method was field tested and used in several countries.
NEW WISN Manual
Access the WISN Tool
Please visit the community of practice (self-registration) to access the software tool.
WISN implementation groups and their roles

Workload Indicators of Staffing Need (WISN) process infographic
WISN methodology infographic
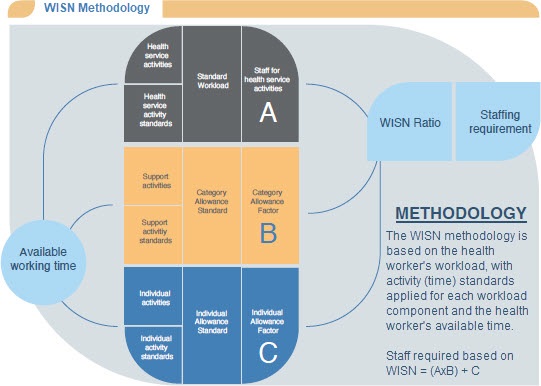
Workload Indicators of Staffing Need (WISN) methodology infographic
Publications
Countries' experiences on implementing WISN methodology for health workforce planning and estimation
Publication of this Human Resources for Health journal supplement was supported by the World Health Organization (WHO). Articles have undergone the journal's standard peer review process for supplements.

Estimating staffing requirements using workload indicators of staffing need at Braun District Hospital...
Papua New Guinea has seen some improvements in health indicators over the past years, but the pace of improvements is not as robust as expected. The Health...

An assessment of existing surge capacity of tertiary healthcare system of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province...
Globally the occurrence of disasters has increased more than fourfold during the last three decades. The main concern for the healthcare system responding...

Multi-country case studies on planning RMNCH services using WISN methodology: Bangladesh, Ghana, Kenya,...
Globally, many countries are adopting evidence-based workforce planning that facilitates progress towards achieving sustainable development goals for reproductive,...

Applying WHO COVID-19 workforce estimate tools remotely in an African context: a case report from Mali...
The COVID-19 pandemic has increased the burden on health systems, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, where health systems already struggle....
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4 (current)
- 5
