WHO Results Report - Programme Budget 2018-2019

•
key achievements
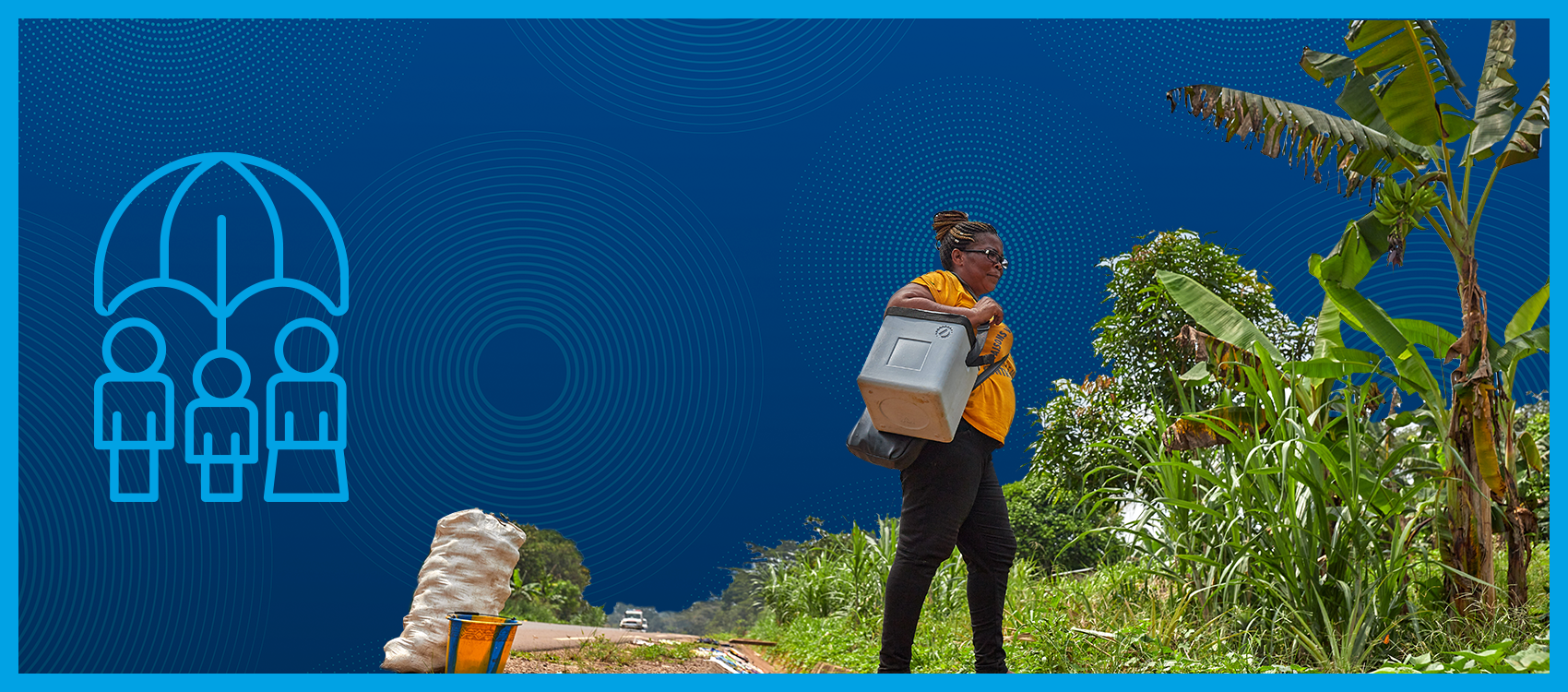
Universal health coverage based on primary health care is a unifying concept; a platform for integrated, people-centred delivery of health services; and one of the most powerful social equalizers among all policy options.
HIGH-LEVEL COMMITMENT TO UNIVERSAL HEALTH COVERAGE
The political declaration of the high-level meeting on universal health coverage of 2019 is the most comprehensive instrument ever adopted by the United Nations on the right of all people to access health services.
The adoption of the Declaration of Astana underscores the importance that world leaders have placed on achieving universal health coverage and related objectives under Sustainable Development Goal 3.
STRONGER AND BETTER PREPARED HEALTH SYSTEMS
The Joint Working Team for Universal Health Care programme focuses on health systems strengthening for primary health care and essential public health functions. It provided intensified support to South Sudan to build its health system to provide core health services and be prepared for emergencies.
BETTER HEALTH WORKFORCE DATA
The implementation of National Health Workforce Accounts allows countries to compile data across sectors. Currently, 193 countries have data within the past 5 years, compared with less than 100 countries before implementation.
PREQUALIFICATION HELPS PROVIDE QUALITY-ASSURED PRODUCTS TO MILLIONS
During the 2018–2019 biennium, 326 products were prequalified including human insulin, 2 polio vaccines, an Ebola virus vaccine- the fastest vaccine prequalification process conducted by WHO, and many others, providing guidance on the quality, safety and efficacy or performance of health products.
PRESSING FOR VALUE-FOR-MONEY IN ESSENTIAL MEDICINES
More than 150 countries use WHO’s Essential Medicines List to guide decisions about which medicines represent the best value-for-money, based on evidence and health impact.
WHO STAYING AHEAD OF THE CURVE
The establishment of the Science Division, launch of a compendium of target product profiles, and development of an interim guidance on gene editing ensures that WHO can fully exploit the power of science and innovation to deliver impact.
DIGITAL HEALTH AND THE NEXT GENERATION OF INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS
WHO’s draft global strategy on digital health offers a framework for action to facilitate international collaboration in regulating, benchmarking and certifying artificial intelligence and digital health medical devices in order to achieve health for all.
The eleventh revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-11) includes new codes for new types of cancer and allergies. About 70% of the systems that manage health expenditure and resource allocation use ICD as their base.

Approved Programme budget
US$ 590 million

Funds available:
US$ 617 million
(105% of Programme budget)

Expenditure:
US$ 558 million
(95% of Programme budget;
90% of available resources)

health systems









 Back to homepage
Back to homepage