Improving data on foodborne trematode infections and identifying endemic and high-risk areas
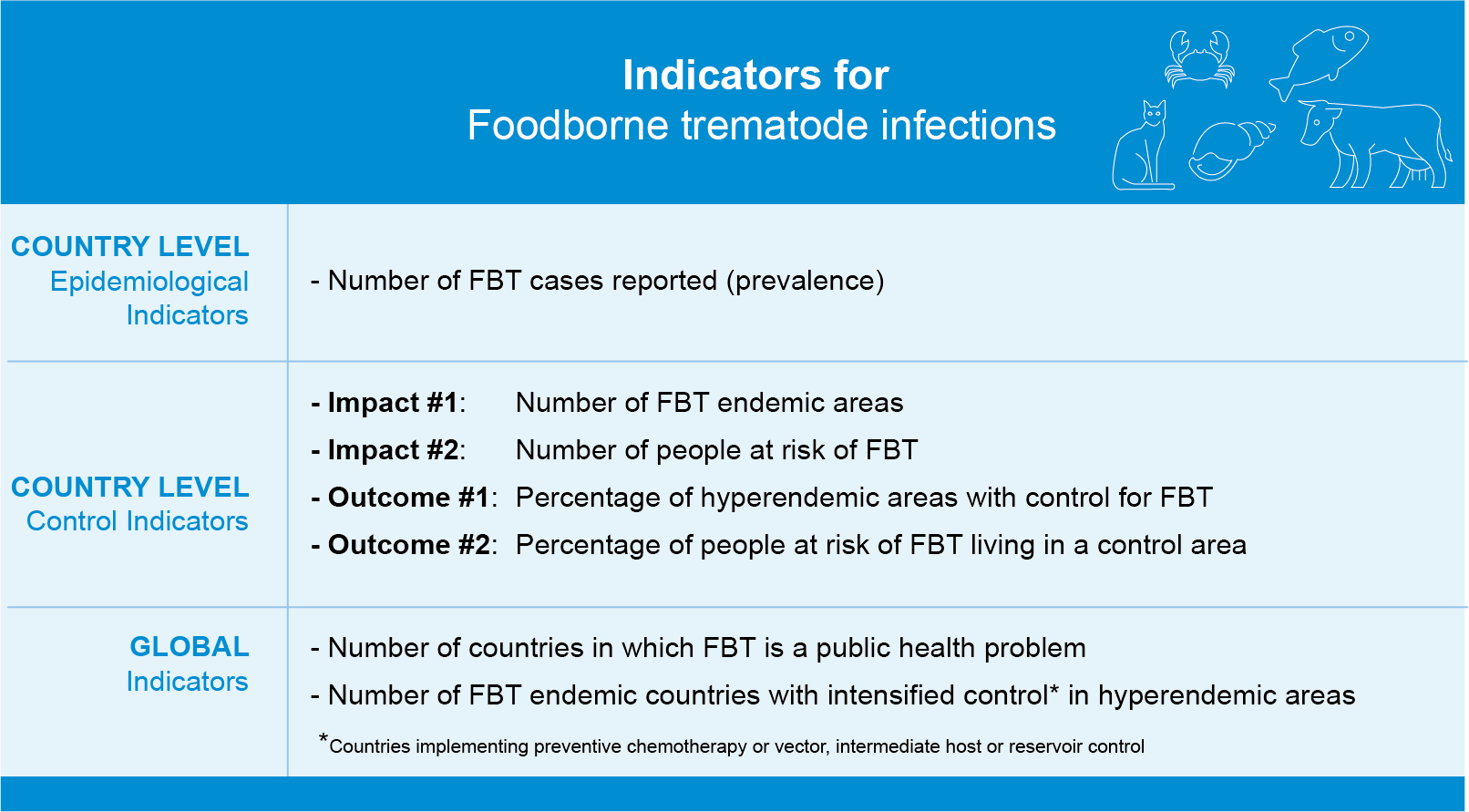
As for other neglected diseases, data on foodborne trematodiases is scarce. Surveillance data is important for understanding disease epidemiology and risk factors, identifying affected populations, and monitoring interventions.
WHO works closely with WHO collaborating centres and other academic and research institutions in developing accurate diagnostics, surveillance and mapping tools. WHO promotes systematic reporting of epidemiological and treatment data within countries and from countries to WHO to improve surveillance of foodborne trematode infections.