
ABOUT THE CAMPAIGN
#BeatDiabetes is a WHO initiative to increase awareness about diabetes and promote a healthy lifestyle.
ABOUT DIABETES
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar. Hyperglycaemia, or raised blood sugar, is a common effect of uncontrolled diabetes and over time leads to serious damage to many of the body's systems, especially the nerves and blood vessels.
In India there are estimated 77 million people above age of 18 years are suffering from diabetes (type 2) and nearly 25 million are prediabetics (at a higher risk of developing diabetes in near future). More than 50% of people are unaware of their diabetic status which leads to health complications if not detected and treated early. Adults with diabetes have a two- to three-fold increased risk of heart attacks and strokes. Combined with reduced blood flow, neuropathy (nerve damage) in the feet increases the chance of foot ulcers, infection and eventual need for limb amputation. Diabetic retinopathy is an important cause of blindness, and occurs as a result of long-term accumulated damage to the small blood vessels in the retina. Diabetes is among the leading causes of kidney failure.

RISK FACTORS
There are many modifiable and non-modifiable factors that cause diabetes.These include:
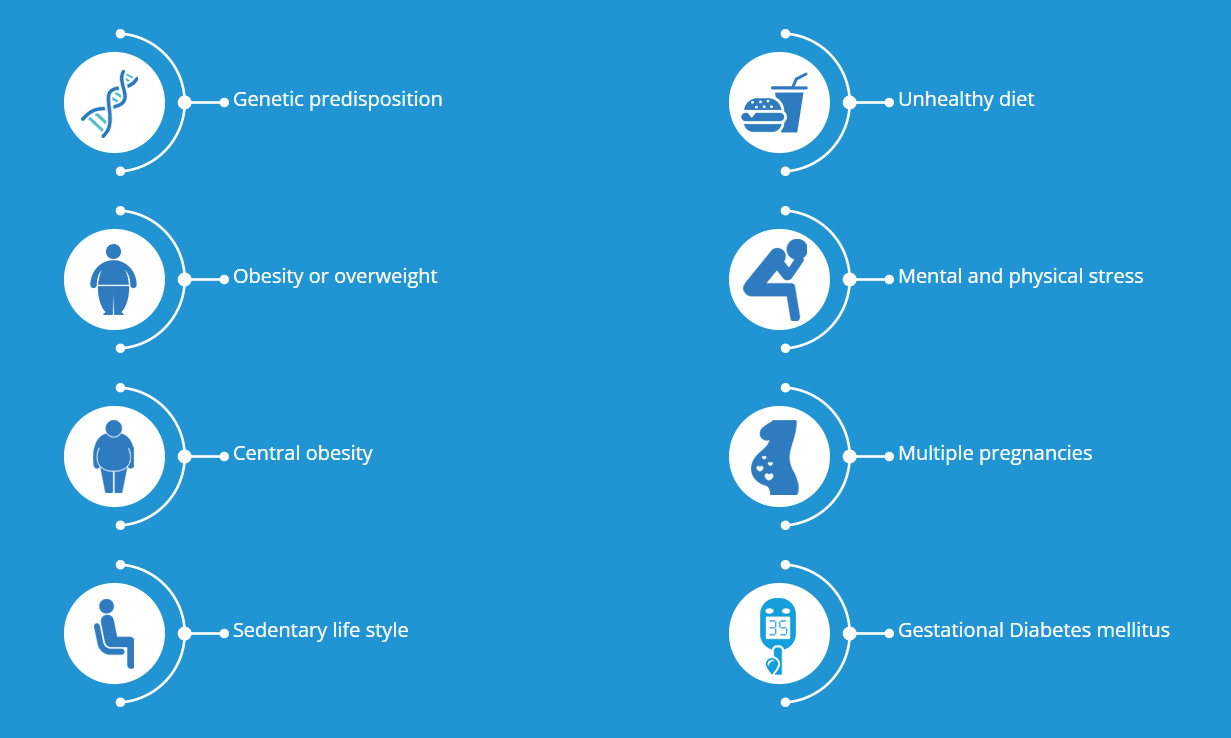
PREVENTION
Nearly 80% of type 2 diabetes is preventable. Simple lifestyle measures have been shown to be effective in preventing or delaying the onset of type 2 diabetes.
To prevent type 2 diabetes and its complications, people should:
- Achieve and maintain a healthy body weight
- Be physically active – doing at least 30 minutes of regular, moderate-intensity activity on most days. More activity is required for weight control
- Eat a healthy diet, avoid refined sugar and saturated fats
- Don't use tobacco. Smoking and chewing tobacco increases the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT

All adults more than 30 years should get their blood glucose levels checked annually at the nearest health facility.
Signs and symptoms may include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Tiredness
- Weight loss
- Excessive hunger
- Non-healing wounds
The health care provider will advise on healthy lifestyle interventions and /or medications based on blood glucose levels. Blood glucose control, particularly in Type 1 diabetes, requires insulin. People with Type 2 diabetes can be treated with oral medication,
but may also require insulin.




