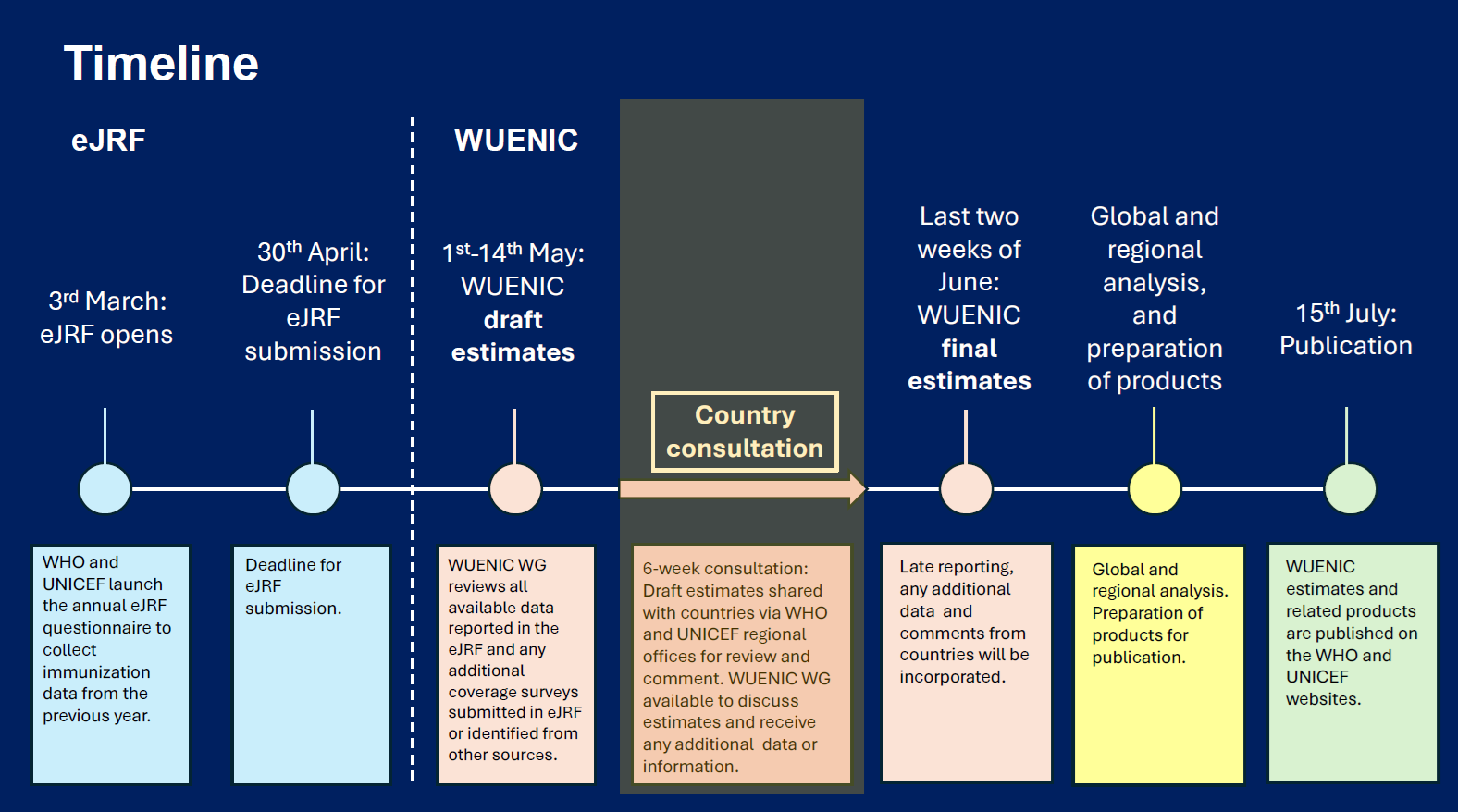
The electronic Joint Reporting Form (eJRF) serves as the primary source for vaccination coverage data globally, which WHO-HQ and UNICEF-HQ jointly compile to produce the WHO-UNICEF Estimates of National Immunization Coverage (WUENIC). WUENIC estimates are crucial in guiding and evaluating immunization programs and assessing progress in eliminating and controlling vaccine-preventable diseases in all Member States of the WHO South-East Asia Region (SEAR). However, at times, there is limited awareness and understanding among Member States regarding the methodology used for these estimates.
WHO organized an orientation webinar for key stakeholders to enhance understanding and strengthen capacity among Member States on the WUENIC estimation process. The objective of this orientation webinar is to provide awareness and sensitization to the immunization stakeholders of the region on methodology of this estimation process. To encourage active participation from all countries and ensure comprehensive engagement, the webinar was conducted virtually in two batches, allowing WHO to effectively address queries and provide detailed explanations.
Batch 1 on 20th January 2025 from 1300-1500 hours (IST) – Bhutan, DPR Korea, India, Maldives and Nepal
Batch 2 on 21st January 2025 from 1300-1500 hours (IST) – Bangladesh, Indonesia, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Timor-Leste
Member States from all eleven countries of the region actively participated in the webinar, along with over 100 representatives from governments, WHO, UNICEF, and other partner agencies. Following are some key deliberations from the webinar:
Key deliberations from the webinar
The orientation session informed participants that the WUENIC Working Group (WWG), comprising experts from WHO-HQ and UNICEF-HQ, methodology of WUENIC estimates, and review process. WUENIC estimates are derived from reported coverage, national best estimates, coverage surveys, published and grey literature, and contextual factors such as data quality audits, expert opinions, local knowledge, and stockouts.
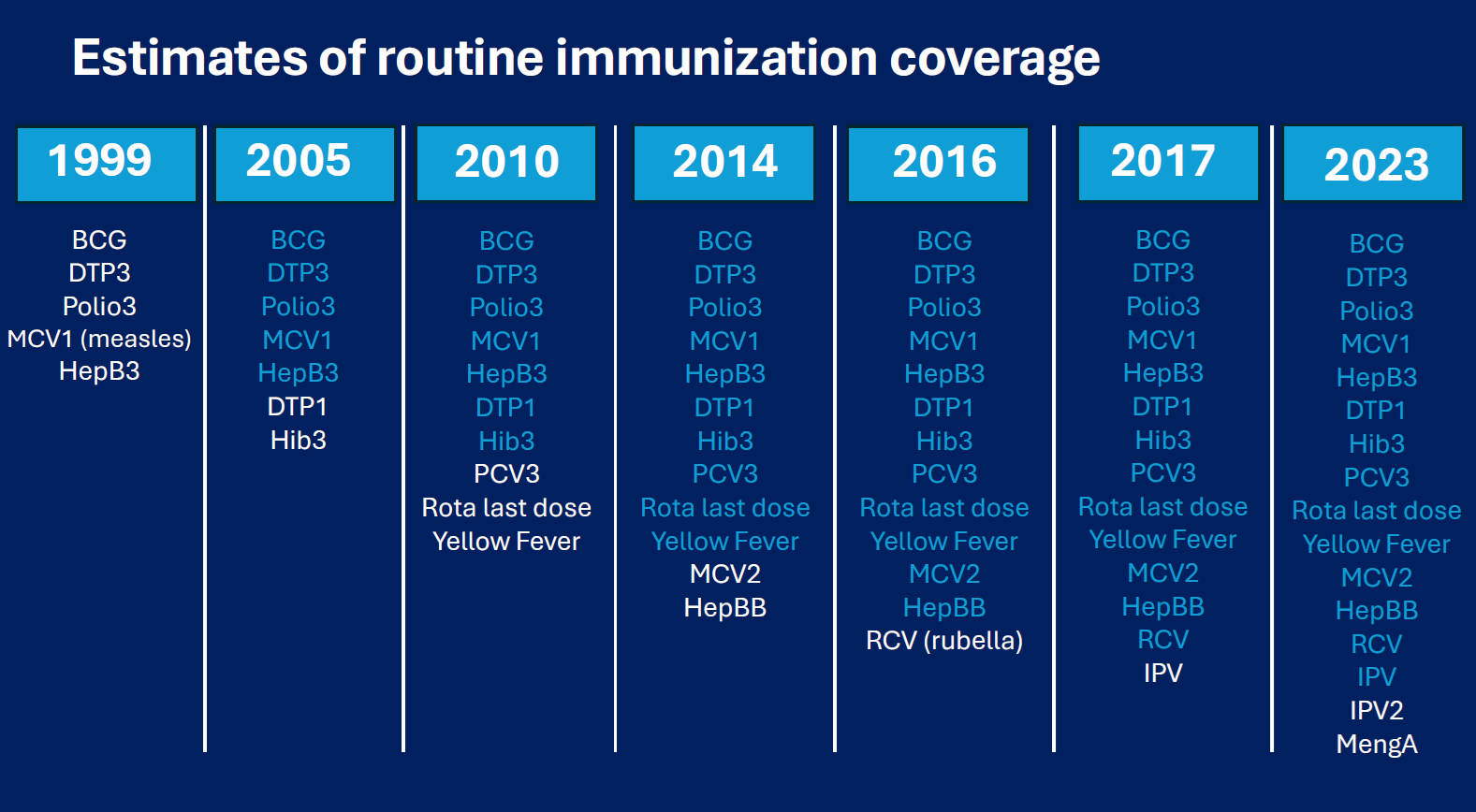
Historical estimates are revised using the most recent data available. Estimates for regional, global, and other country groups are derived from official population estimates and projections by the United Nations Population Division (source: UN Population Division). The WUENIC Methodology Publications are featured in several scientific journals, listed below.
- Burton et al. 2009. WHO and UNICEF estimates of national infant immunization coverage: methods and processes.
- Burton et al. 2012. A formal representation of the WHO and UNICEF estimates of national immunization coverage: a computational logic approach.
- Brown et al. 2013. An introduction to the grade of confidence used to characterize uncertainty around the WHO and UNICEF estimates of national immunization coverage.
- Brown at al, 2015, An examination of a recall bias adjustment applied to survey-based coverage estimates for multi-dose vaccines.
- Danovaro-Holliday at al, 2021 Compliance of WHO and UNICEF estimates of national immunization coverage (WUENIC) with Guidelines for Accurate and Transparent Health Estimates Reporting (GATHER) criteria.
The strengths of WUENIC estimates lie in their use of country-specific data, which ensures contextual relevance, and the incorporation of programmatic information for more accurate projections. Additionally, the Grade of Confidence adds reliability to the estimates. However, there are limitations, as estimates are influenced by the quality of underlying data, and uncertainty is not quantitatively estimated. More recent year estimates often rely on fewer data sources, with earlier years benefiting from more robust survey data. Historical series are revised as new data emerges.
WUENIC products
- Country profiles: https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/wuenic-trends/
- User reference: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/guide-how-to-read-a-country
- Slide decks: https://data.unicef.org/resources/immunization/
- Data and reference materials (WHO website): https://www.who.int/teams/immunization-vaccines-and-biologicals/immunization-analysis-and-insights/global-monitoring/immunization-coverage/who-unicef-estimates-of-national-immunization-coverage

After discussions on WUENIC estimation methodology for different vaccine antigens, methodology of estimation methodology of Human Papillomavirus Vaccine (HPV) coverage was discussed in detail. Like other vaccine antigens numerator for HPV is derived from reported data through eJRF and other data sources. However, denominator is not taken from reported population data but official United Nations population estimates and projections are used as denominator for HPV coverage estimates. Estimation methodology of programme coverage of HPV as a short-term performance and methodology of coverage by age 15 years as long-term performance was explained. Also discussed was the difference and merging of first dose coverage estimate and final dose coverage estimate based on HPV dose schedule in the country.
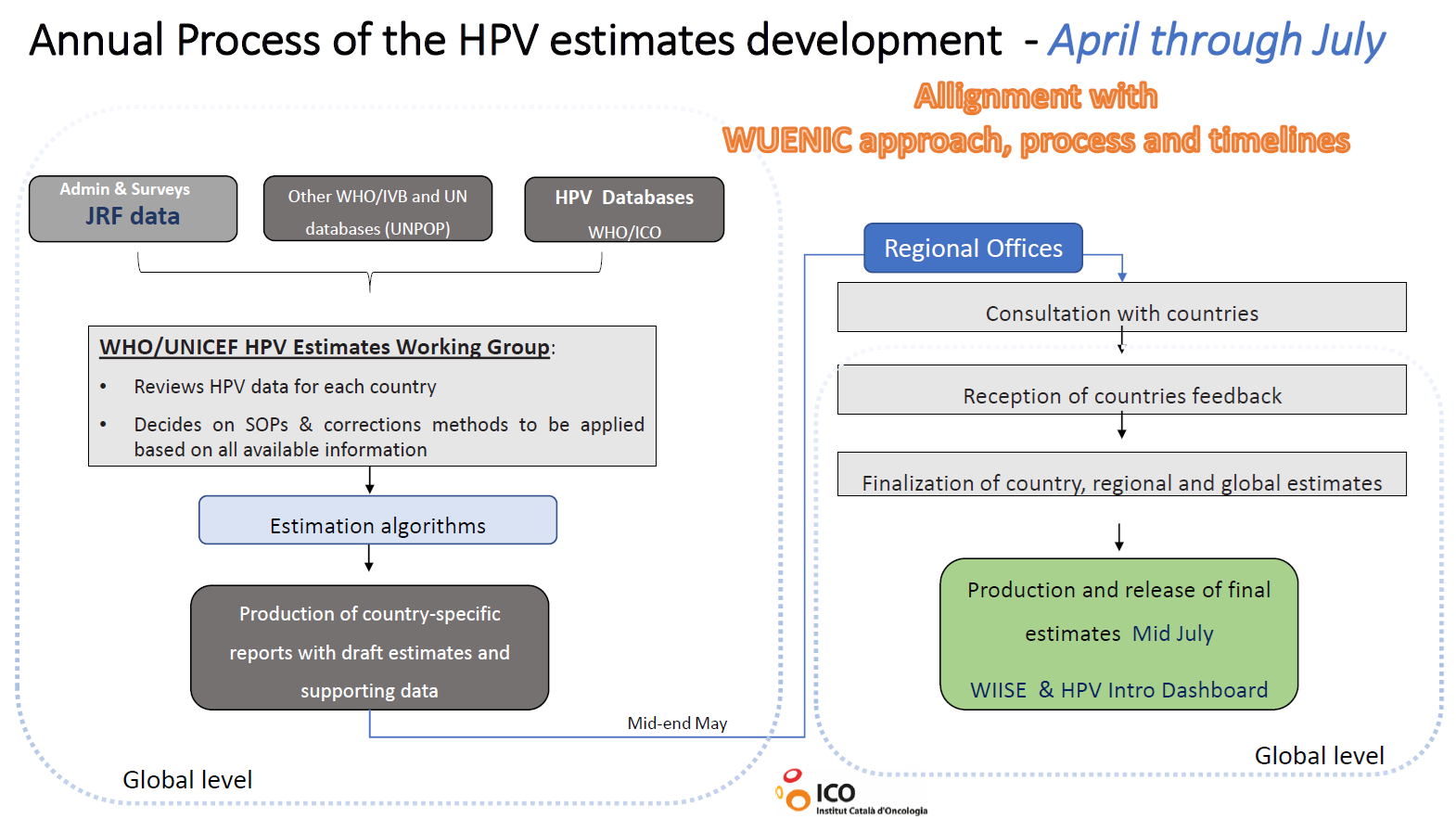
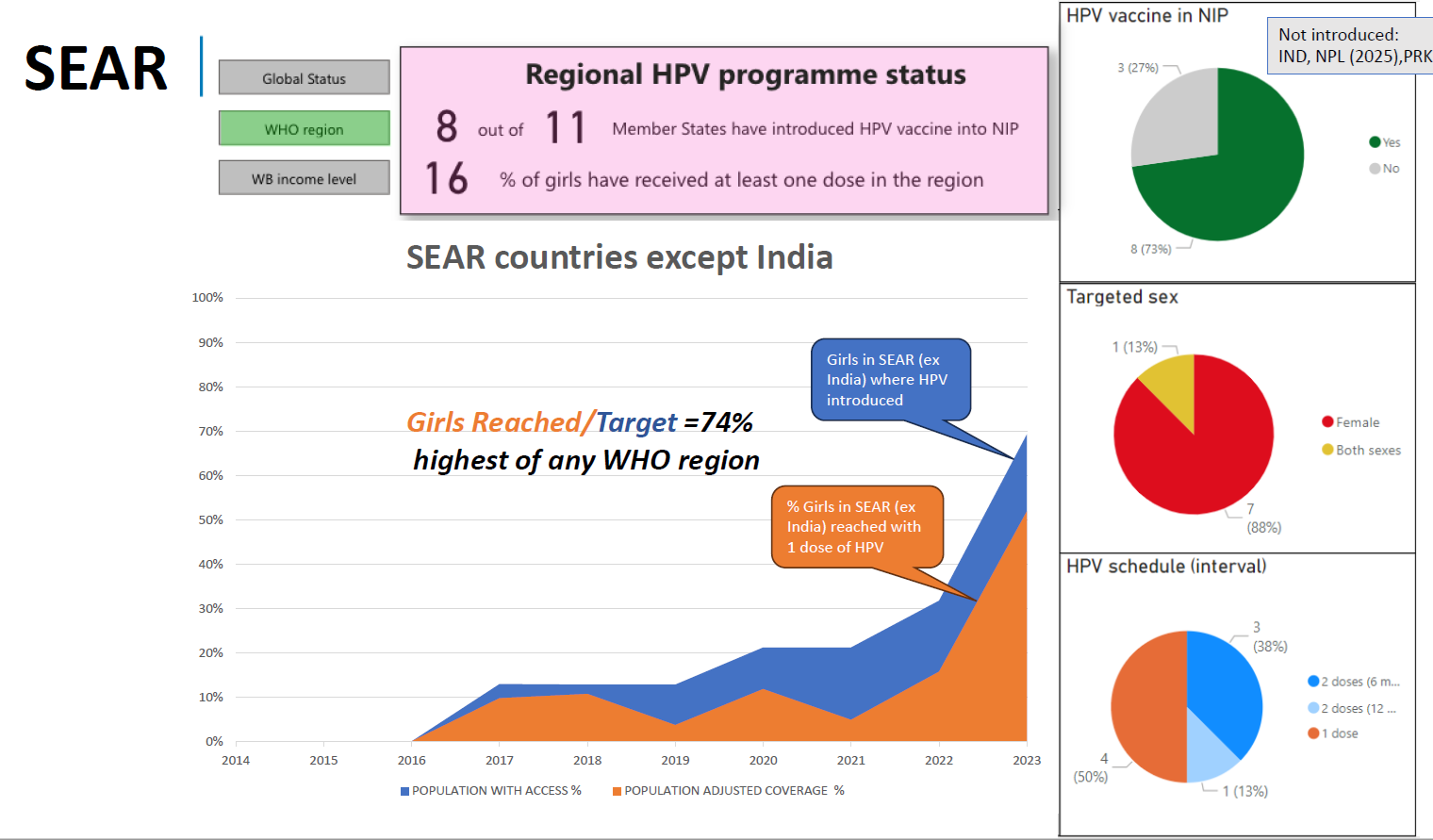
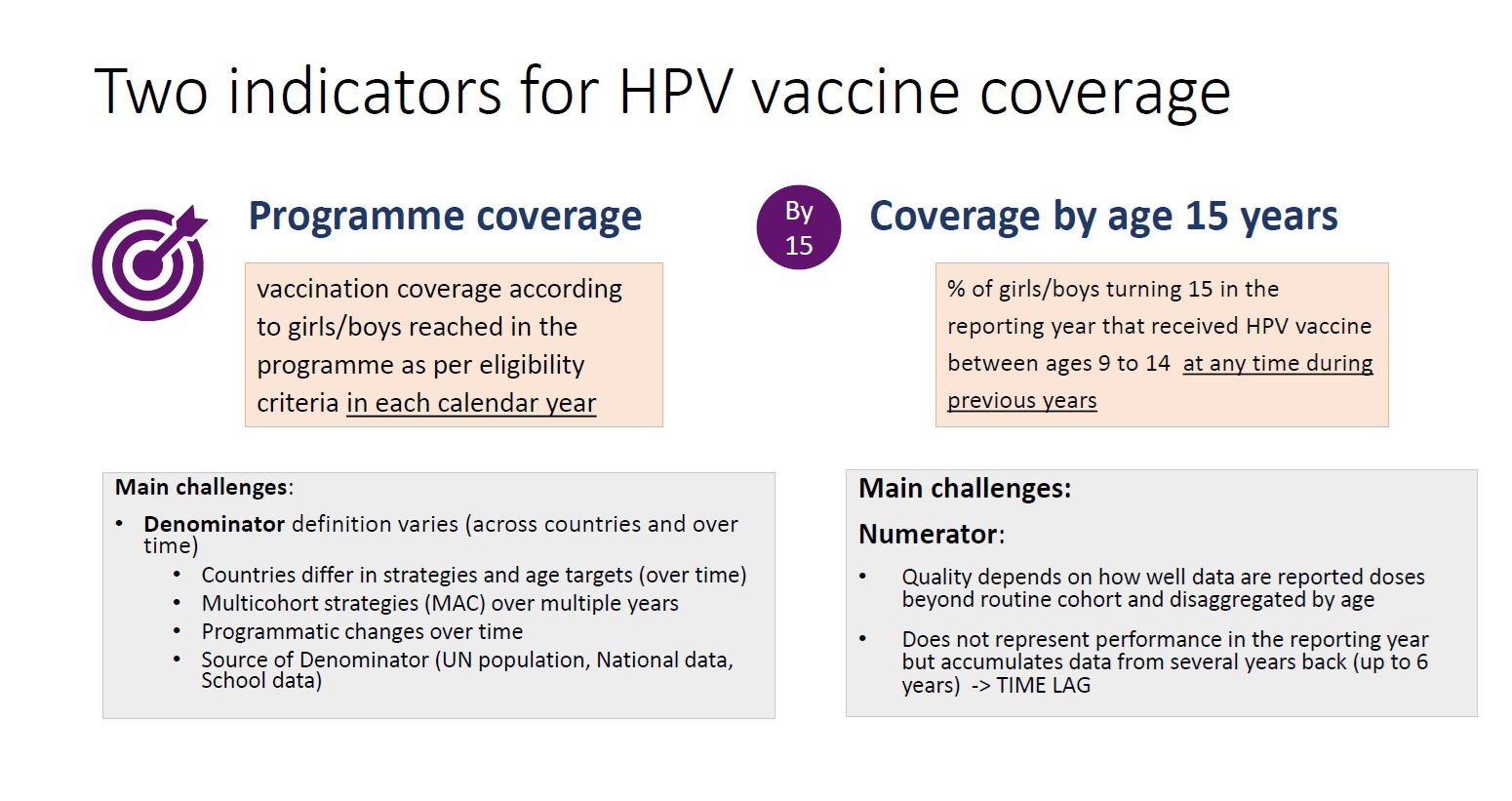
Limitations: Currently, most country HPV coverage estimates are solely based on reported administrative data. To improve the accuracy of these estimates, HPV data from coverage surveys is necessary to triangulate and validate the administrative data, similar to the approach used by WUENIC for childhood vaccines. HPV modules are available for EPI coverage surveys, DHS, MICS, and GSHS. It is crucial to ensure that the HPV vaccine is included in planned coverage surveys to enhance the quality of estimates.
Participants were interactive and there were quite a few queries regarding the methodology of immunization coverage estimation, especially HPV.
