Clinical registries capture detailed information on patient presentation, treatment, and outcomes across the full continuum of care, from prehospital to inpatient settings. By providing integrated data and built-in analytical tools, registries help identify potentially preventable deaths, poor outcomes, and near misses that reveal gaps in care. This enables targeted quality improvement efforts that have been shown to save lives and strengthen health system performance over time.

EQuIP: establishing clinical quality improvement programmes
Overview
Every year, between 5.7 and 8.4 million deaths in low- and middle-income countries are linked to poor quality care. Adverse events from unsafe care are among the top 10 causes of death and disability, with annual costs exceeding USD 13 trillion globally. Achieving universal health coverage requires access to health services which deliver high-quality care and protect people from harm.
WHO supports countries with guidance for national quality policies and strategies to strengthen health system performance across levels of care. Every day, people experience health systems through the quality of clinical care they receive—in their communities, clinics, and health facilities. Quality clinical care must be people-centred, safe, timely, effective, integrated, and delivered efficiently, addressing the realities of the way people present to care.
The Establishing clinical Quality Improvement Programmes (EQuIP) toolkit complements system-level guidance by empowering health providers to design and implement quality improvement initiatives at the point of service delivery. It uses a data-driven approach to identify gaps and barriers to high-quality clinical care, analyse their causes and impacts and select appropriate corrective actions for measurable and sustainable changes. These initiatives may deliver across patient outcomes and experiences while strengthening system efficiency, data use and staff well-being throughout the care continuum.
About EQuIP
EQuIP is based on compelling evidence that simple, well-designed interventions can lead to significant improvements in care quality, reduce preventable deaths and save lives. The EQuIP toolkit builds competencies to address locally identified gaps and barriers to delivering high-quality clinical care by applying structured quality improvement methodology.
EQuIP toolkit is purpose designed to be practical, relevant, and applicable at the point of care across a wide range of clinical programmes. It brings together and updates a wide range of existing work from the WHO on quality of care, including the Trauma Quality Improvement Programme and the Point of Care Quality Improvement initiative. The core content is targeted at managers, experienced health workers, including doctors, nurses, midwives, and paramedical providers.
The toolkit includes:
- EQuIP Learning programme - teaches providers to apply clinical quality improvement methods and promote a culture of quality and accountability in clinical care. Providers will learn how to formulate clear aims for measurable improvements and how to select appropriate interventions and to address problems through iterative implementation and adaptation of quality improvement plans.
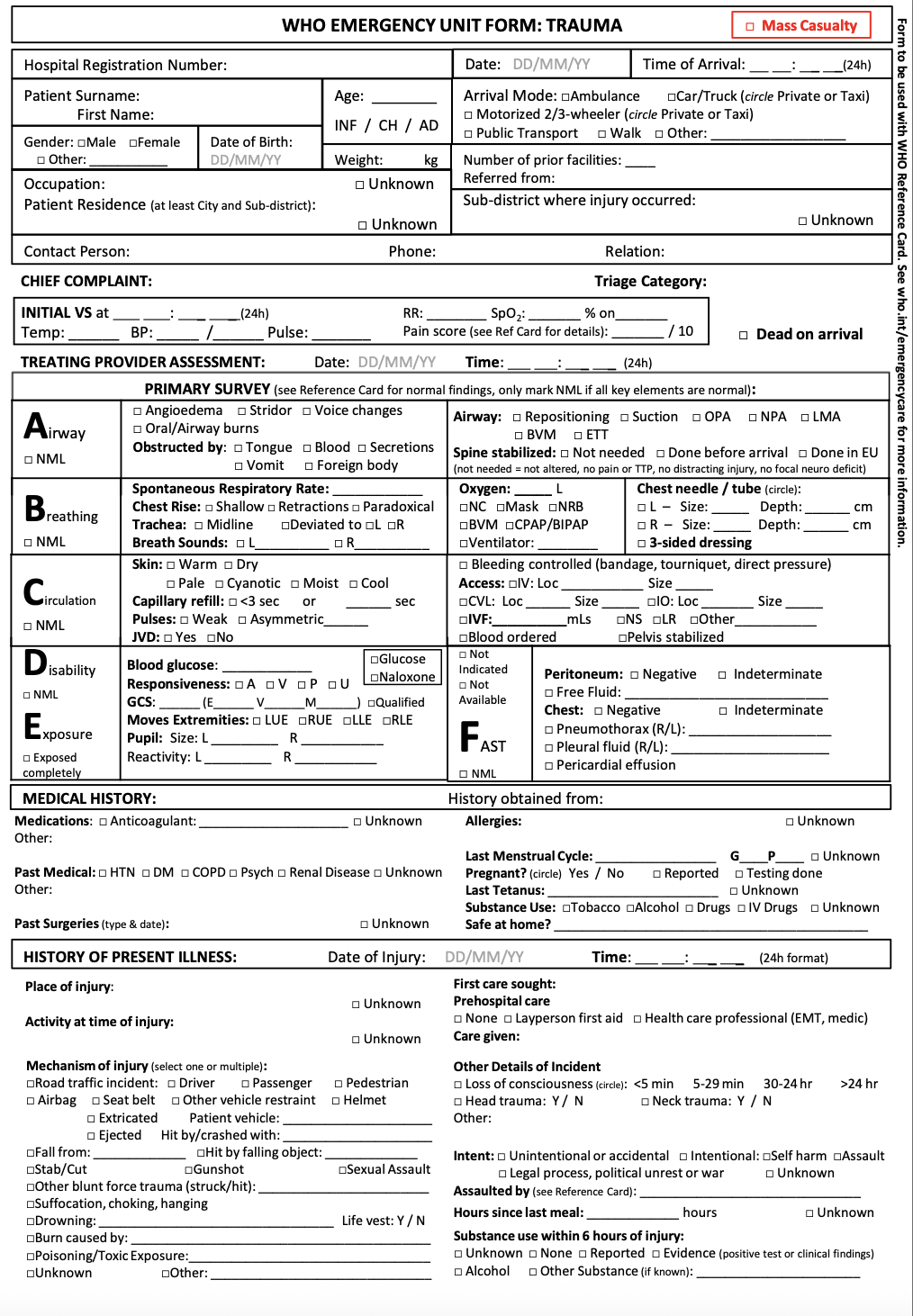
- Tools and templates - facilitate structured QI meetings and use evidence-informed frameworks and diagrams to assess and map structures, processes and outcomes in clinical care. WHO's Clinical Registry provides a platform for standardized case-based data collection with built-in analytics to evaluate care and monitor outcomes.
Tools to improve quality at the point of care
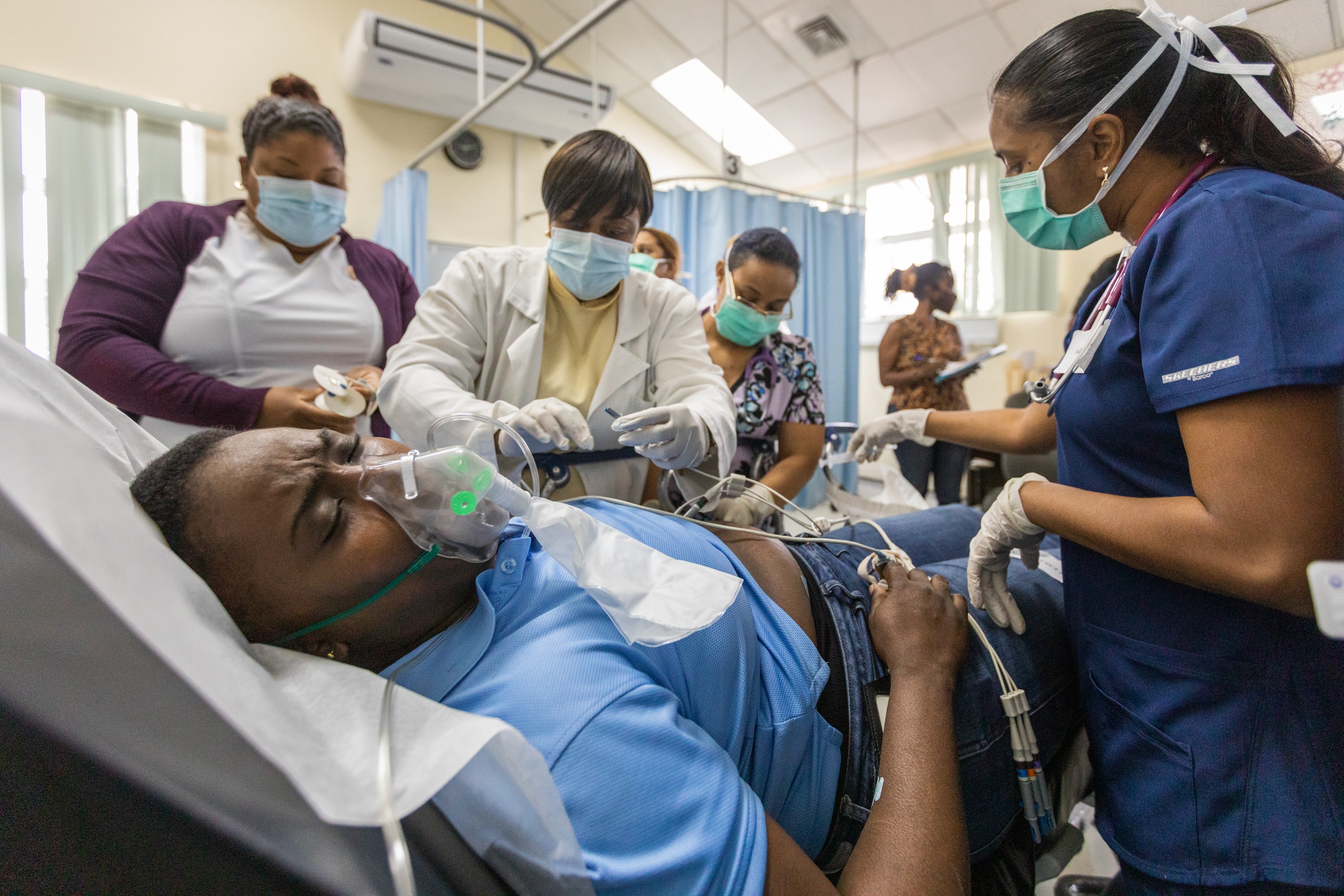
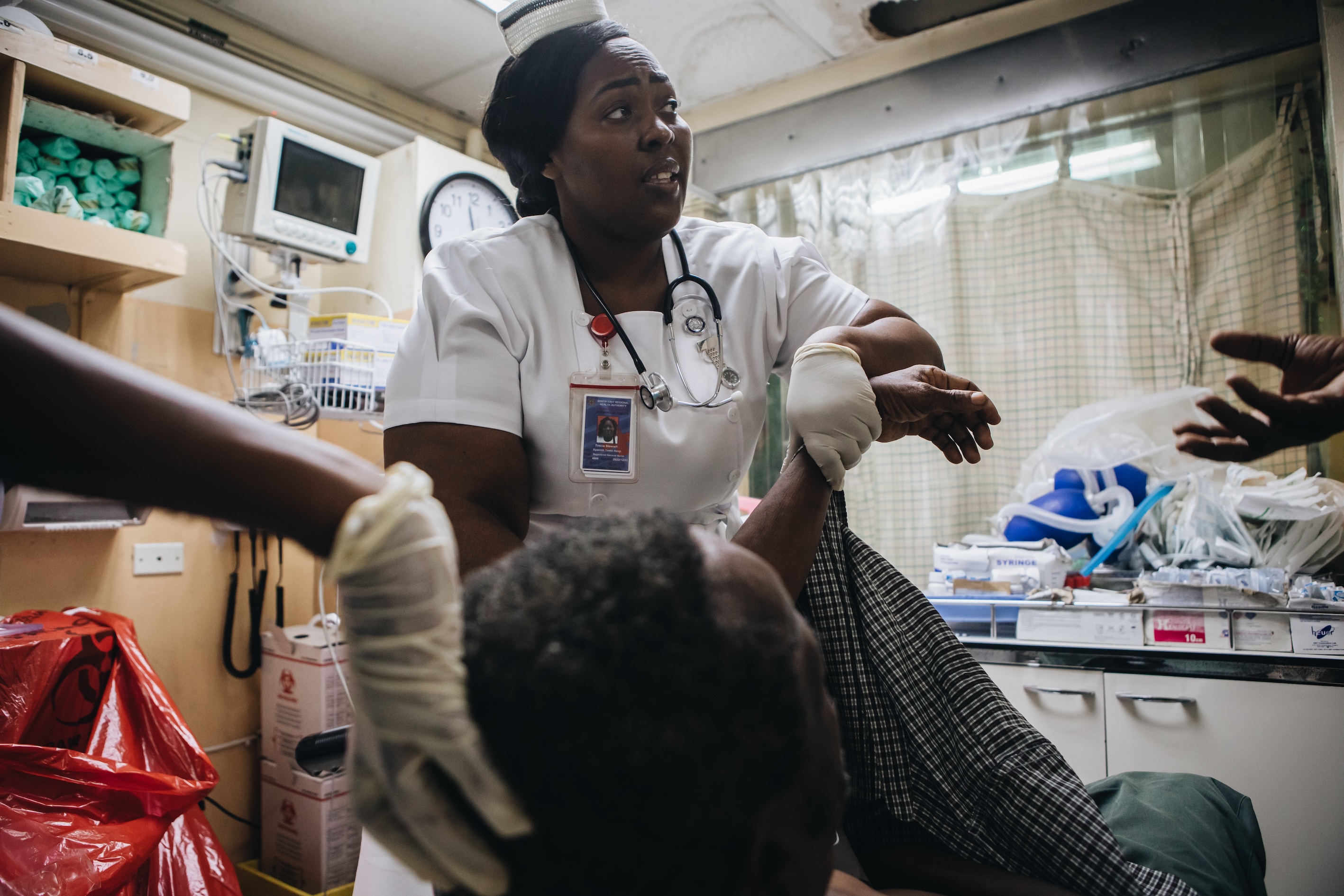
EQuIP is supported by a wide range of clinical process tools and trainings which can help deliver safe and effective care to the ill and injured. Together these resources equip teams to apply proven quality improvement methods and drive gains in patient outcomes.
Strengthen the use of data for quality improvement and system planning
Use clinical registries to identify gaps in care, drive quality improvement, and strengthen health system performance.

Improve systematic documentation and data collection.

Enhance timeliness of care
Build health care worker capacity and competency
Provide effective, context-appropriate pre-service and in-service capacity building for providers.
Strengthen clinical effectiveness via improved processes of care
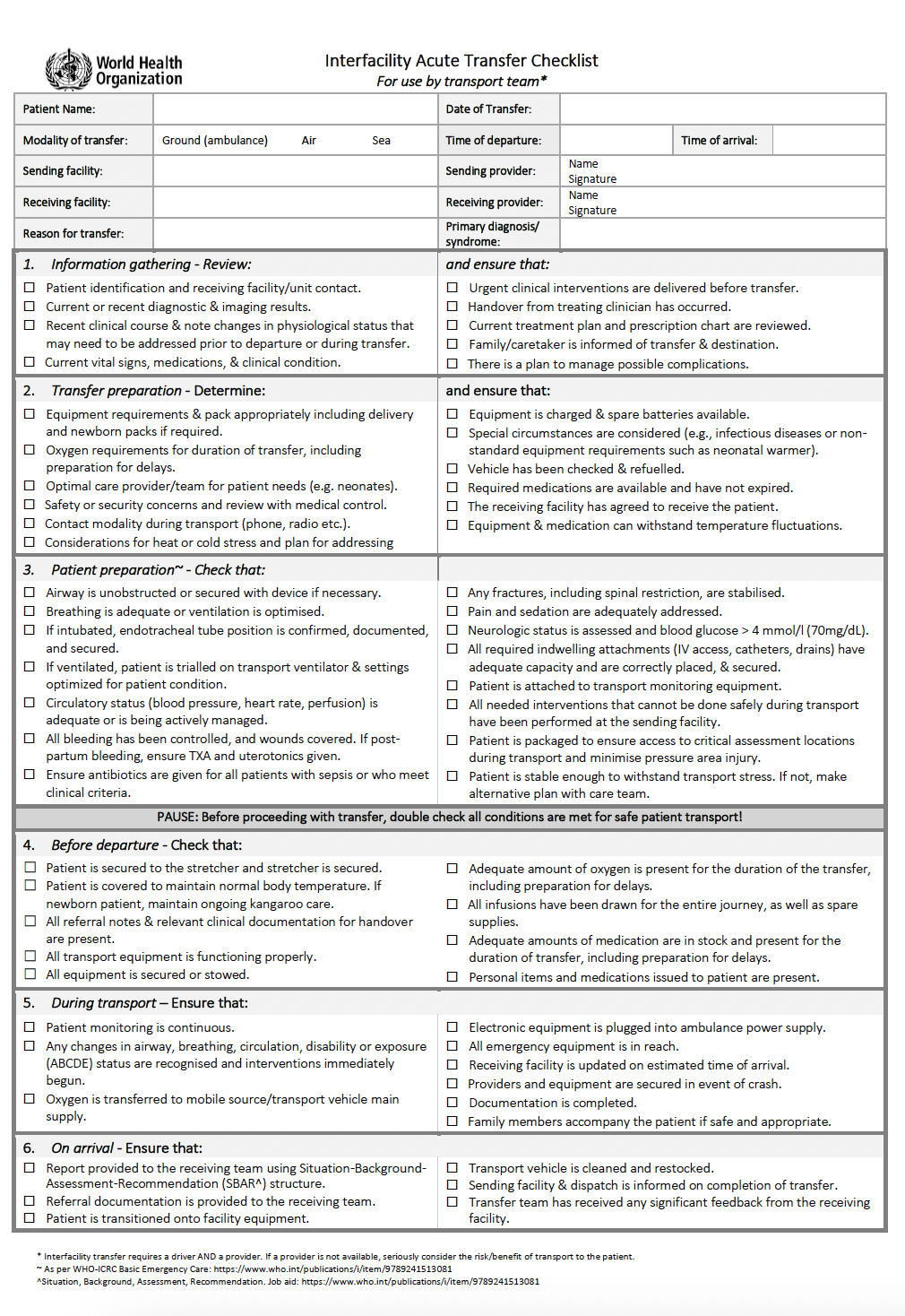
Use checklists to minimise missed conditions, errors, and adverse events.
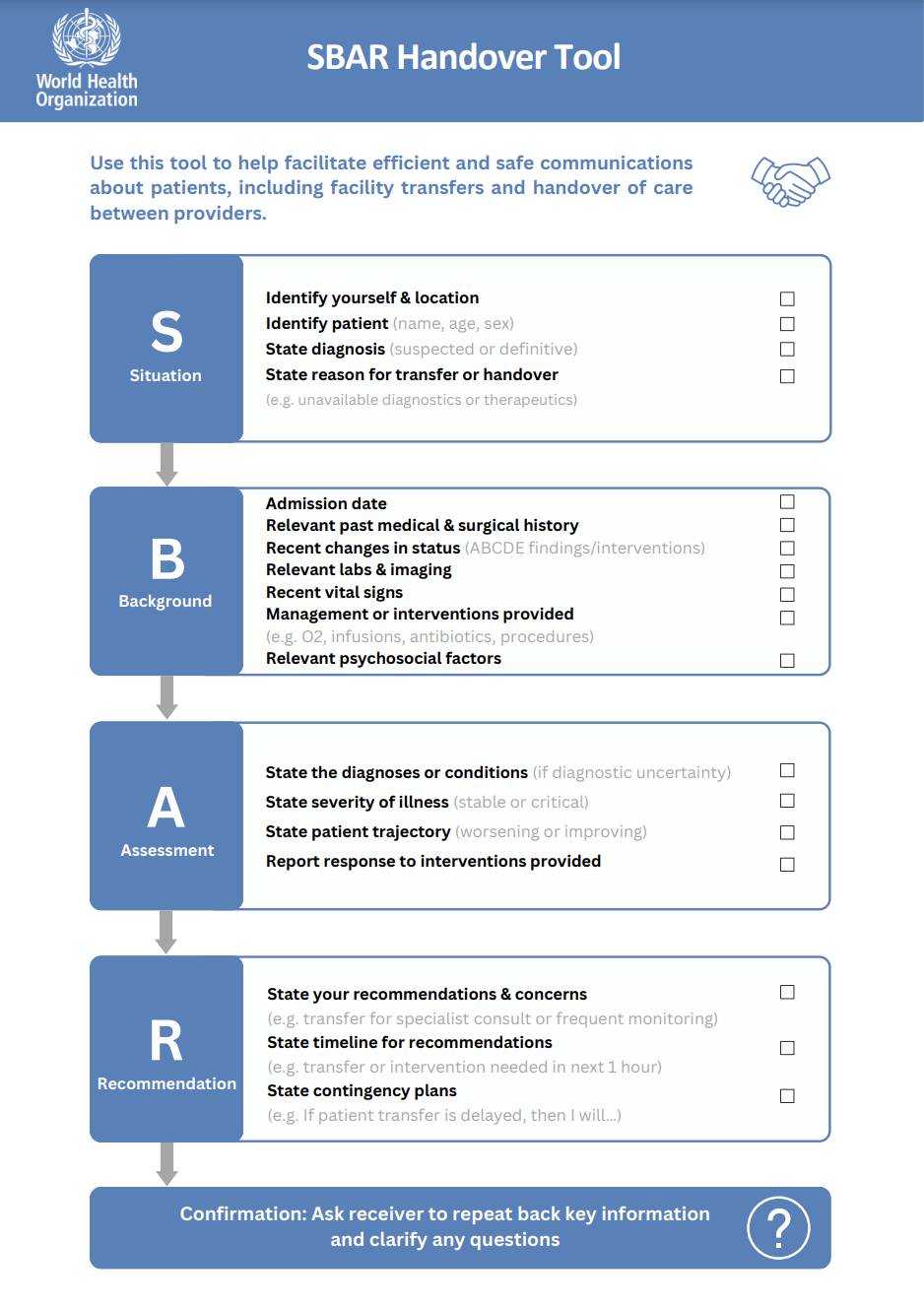
Advance team communication and coordination
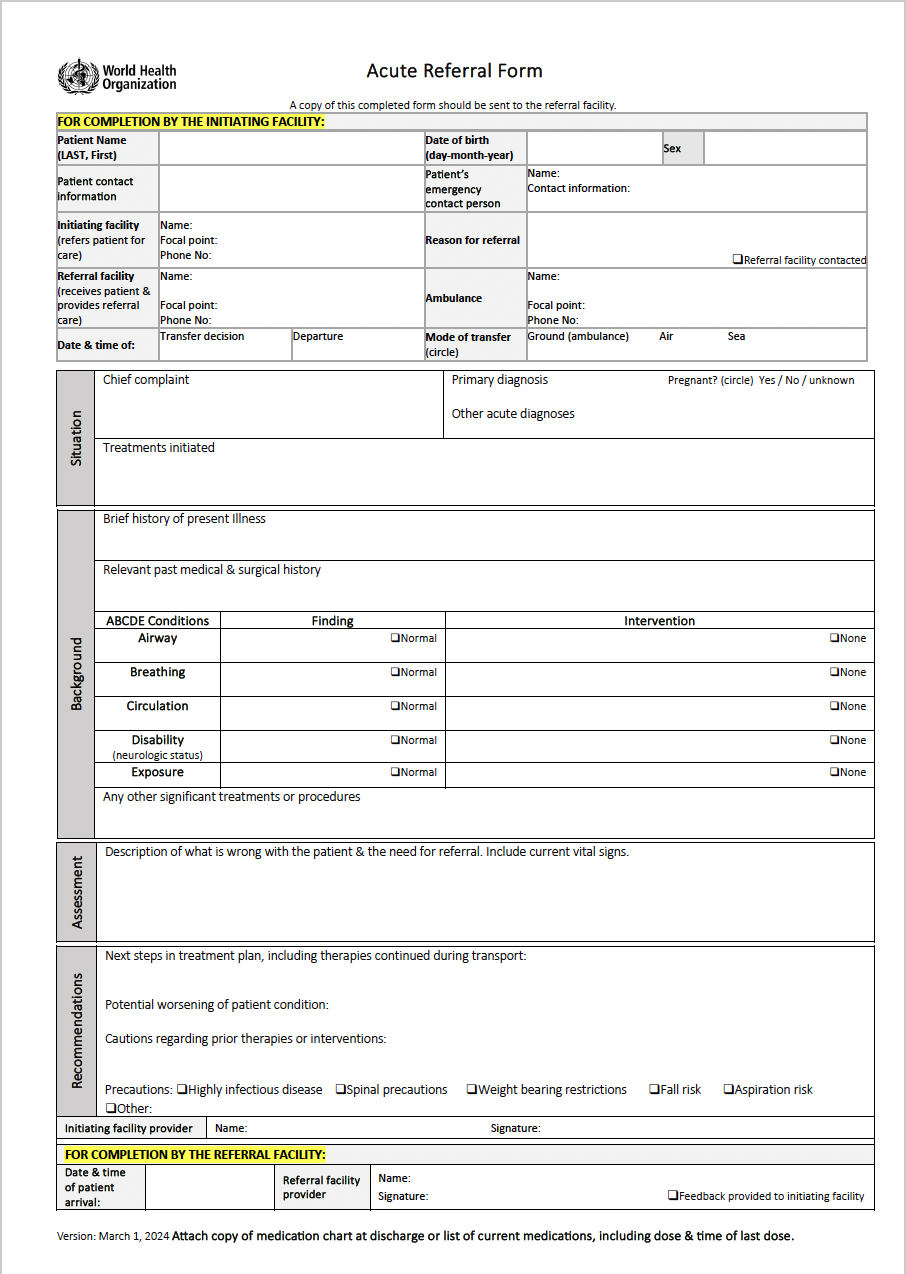
Promote effective patient handover between providers.
Ensure safe referral and transfer between units or facilities.