Working with countries to mitigate disruption in provision and use of MNCAH services in context of COVID-19 pandemic
The WHO Department of Maternal, Newborn, Child and Adolescent Health and Ageing (MCA) has worked with a set of countries to mitigate the indirect impact of COVID-19 on essential health services, more specifically to ensure the continuity of essential services for maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health (MNCAH). Some countries have additionally focused on services for reproductive health and ageing. The initiative has supported Ministries of Health in their role of coordinating national implementing partners to ensure a focus on women, newborns, children, adolescents and older people during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The initiative brings together a team at the regional and country levels whose role is to connect and engage with a national Technical Working Group on MNCAH and COVID-19. These groups include government representatives, implementing partners and stakeholders, working in close collaboration with national COVID-19 response structures. Each country team has documented strategies and guidance developed and actions implemented to maintain the delivery and utilization of essential MNCAH services and prevent disruptions in health services due to COVID-19. The WHO team has supported country teams to collect, synthesize and analyze information, supported the use of data for decision-making, facilitated policy dialogues at the country level and organized opportunities for cross-country learning.
The initial phase of the initiative began in May 2020 and included 19 countries in five of the WHO regions. The overall aim of the first phase was to support countries in developing their optimal response to COVID-19 including strategies to reduce the indirect effects on pregnant women, newborns, children and adolescents due to service disruption. Building on the achievements of the first phase, lessons learned and priorities identified by countries, the initiative was continued for a next phase. The second phase includes 15 countries from all six of the WHO regions. In this phase of the initiative, WHO continues to support countries in building back better and resilient health systems and ensure the needs of MNCAH are at the core of public health services and integrated into future emergency preparedness and response plans of countries.
Focus countries
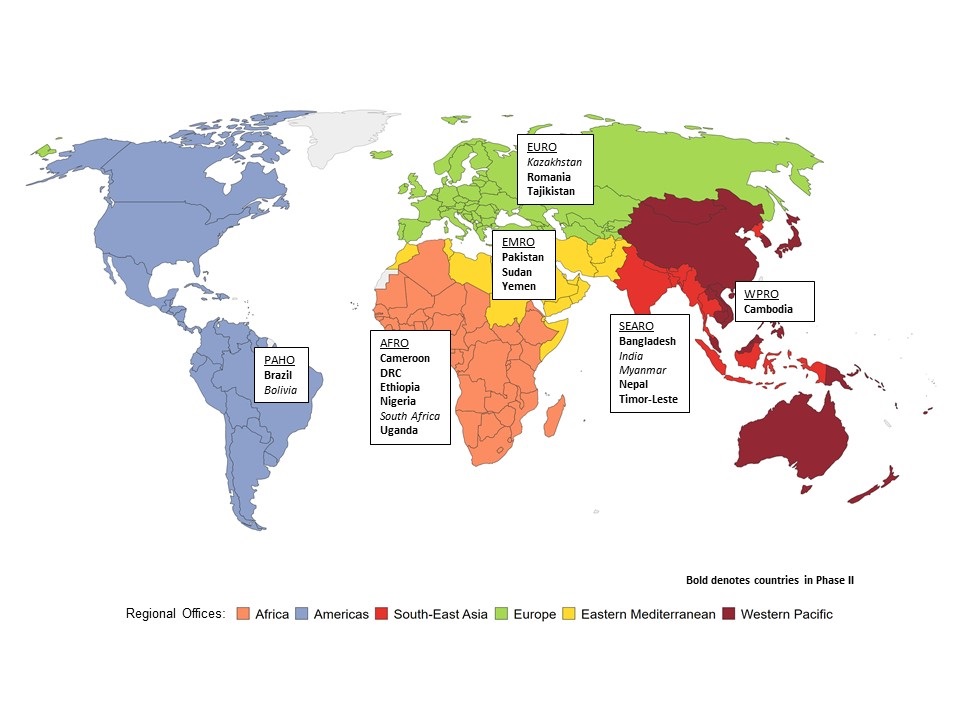
MCA and COVID-19 mitigation initiative map with BMGF countries
Area of work - Data for monitoring
Monitoring the delivery and utilization of health services using data from routine health information systems is critical for understanding in a timely manner the extent of disruption to essential MNCAH services due to COVID-19. Analysis and visualization can help to better use these data to inform decision-making and action. The WHO team and national consultants collaborated with Ministries of Health to identify indicators reported routinely through their national health management information systems to monitor effects of COVID-19 on essential services for reproductive, maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health and nutrition.
Analysing and using routine data to monitor the effects of COVID-19 on essential health services – Practical guide for national and subnational decision-makers was developed by WHO and partners to support country monitoring to inform programme adjustments meant to ensure essential health service availability. Within this resource, a module on RMNCAH, including nutrition and immunization, focuses on using existing routine data to identify changes to utilization of RMNCAH services. The module also includes suggestions on analyzing and interpreting these data and using these data to inform planning and decision-making.
Accompanying the guidance document, an
Excel template provided to compile MNCAH data from national health
management information systems and generate visual dashboards.
Several pulse surveys and rapid assessments to assess disruptions to service delivery and utilization of essential health services were conducted by WHO and other agencies since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Results of the responses to questions on perceived disruptions to RMNCAH services from these surveys were compiled and provided to each country.
- Pulse survey on continuity of essential health services during the COVID-19 pandemic: interim report, 27 August 2020
- Third round of the global pulse survey on continuity of essential health services during the COVID-19 pandemic: November – December 2021
How this contributed to the TWG and dialogue on mitigation strategies:
This work helps countries assess the impacts of COVID-19 on MNCAH using various data sources. Dashboards from national HMIS data visualize month-to-month changes in delivery and utilization of MNCAH services, allowing for an informed understanding of recent disruptions to and recovery of specific services. These data monitoring activities have supported Technical Working Groups in reviewing data regarding periods of disruption of essential services, facilitated country dialogue and informed planning of priorities and mitigation actions.
Area of work - Modelling to assess impact
Work was undertaken to determine how to best use modelling of indirect impacts of COVID-19 on MNCAH health outcomes for advocacy and decision-making. Existing tools, such as the Lives Saved Tool (LiST), were used to assess how disruptions to health services and delivery of high-impact interventions might impact morbidity and mortality of women and children.
A new risk-benefit assessment tool was also developed to assess the risk of contracting COVID-19 when visiting a health facility versus the benefit of receiving the service.
This new tool can assist in informing decisions on maintaining essential health services. Several countries are working on developing and refining this tool. Once finalized the tool can be used not only for COVID-19 but for any future epidemics that might restrict access to health services.
Resources and tools
Modelling the health impacts of disruptions to essential health services during COVID-19 – Module 1: Understanding modelling approaches for sexual, reproductive, maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health, and nutrition was developed as a guide providing an overview and description of models used to assess the potential impact of disruptions to essential health services caused by COVID-19 on morbidity and mortality from conditions other than COVID-19 illness. The guide presents models that have been used to assess these indirect impacts and have applications for the purposes of planning and development of policies and programmes.
The Lives Saved Tool is a modelling tool designed to estimate the impact of coverage changes of health interventions on mortality in a country. LiST has been used by planners and policy makers to understand the impact of implementing different packages of interventions, i.e., the number of lives saved, including during COVID-19.
The risk-benefit assessment model has been used to compare lives saved through continued provision of essential services versus lives lost due to increased exposure to the virus.
Documentation of response and lessons learnt
WHO headquarters, regional and country teams collaborated to collect and synthesize strategies and actions undertaken to maintain essential MNCAH services. The documentation of strategies, lessons, successes and challenges contributes to policy dialogues at the country and regional levels including with national Technical Working Groups to safeguard MNCAH services. The initiative also aimed to capture experiences of stakeholders in countries during the pandemic, acknowledging the importance of understanding stakeholders’ experiences and perspectives during a health emergency and addressing them in decision-making for response measures.
National Technical Working Groups with the support of the WHO identified strategies they perceived as most important to mitigating the indirect impact of COVID-19 on MNCAH services and those most likely to be continued or discontinued after the pandemic. The regional and country teams prioritized strategies and innovations for in-depth documentation and analysis for integration into countries’ routine service delivery and emergency response plans and for sharing of key lessons from the initiative across countries, regional and global levels.
This documentation will also support countries in updating country preparedness and response plans to ensure MNCAH is integrated.
Key action briefs
English
French
Scoping review
Scoping review of interventions to maintain essential services for maternal, newborn,...
To support countries in
adapting their response to different COVID-19 scenarios, a scoping review
of published and grey literature was conducted to
identify interventions implemented to maintain the provision and use
of essential services for MNCAAH during disruptive events and to summarize
lessons learned during these interventions. The review included
outbreaks of Ebola virus disease (EVD), severe acute respiratory syndrome
(SARS), Zika virus disease (ZVD), the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, and
natural disasters and humanitarian emergencies that caused disruption to
services, transport and other activities.
WHO resources on maintaining essential health services
WHO has developed several resources to support countries in safeguarding essential MNCAH services.
- Maintaining essential health services: Operational guidance for the COVID-19 context interim guidance
- Community-based health care, including outreach and campaigns, in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic: Interim Guidance
- Protection of health and safety of health workers: Checklist for healthcare facilities
- Implementation guide for health systems recovery in emergencies: Transforming challenges into opportunities
Other resources

