Coordinating laboratory networks
Overview
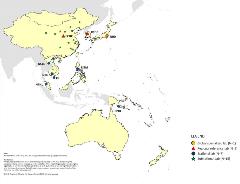
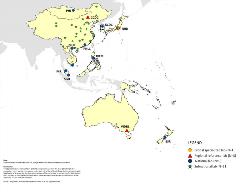
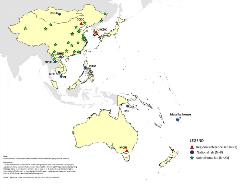
The laboratory networks were established to provide accurate and timely laboratory confirmation of infections, an essential component of disease surveillance systems. The laboratory networks provide high-quality surveillance data to help guide disease eradication, elimination and control programmes. WHO coordinates five vaccine preventable diseases (VPDs) laboratory networks in the Western Pacific Region to support surveillance for selected VPDs, including polio, measles and rubella, Japanese encephalitis (JE), rotavirus and invasive bacterial vaccine preventable diseases (IB-VPD).
The goals of the laboratory networks are to:
- Provide evidence of burden of disease and vaccine introduction.
- Contribute significantly to the evaluation of disease eradication, elimination and control.
- Confirm outbreaks.
- Strengthen quality assurance in participating labs.
WHO Western Pacific Regional Office convenes regular meetings with technical advisory groups (TAGs), representatives from partner organizations, participants from countries and areas in the Region, and WHO staff. The meetings review progress, identify current challenges, and discuss ways in which to strengthen performance.
Key facts
43 accredited polio laboratories in the Western Pacific Region.
65 accredited measles and rubella laboratories in the Western Pacific Region.
19 accredited Japanese encephalitis laboratories in the Western Pacific Region.

/59748.tmb-300v.png?sfvrsn=9885965b_2)